Nuclear receptors rock around the clock
- PMID: 24737872
- PMCID: PMC4210094
- DOI: 10.1002/embr.201338271
Nuclear receptors rock around the clock
Abstract
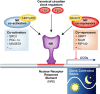
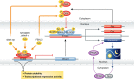
Circadian rhythms characterize almost every aspect of human physiology, endocrinology, xenobiotic detoxification, cell growth, and behavior. Modern lifestyles that disrupt our normal circadian rhythms are increasingly thought to contribute to various disease conditions ranging from depression and metabolic disorders to cancer. This self-sustained time-keeping system is generated and maintained by an endogenous molecular machine, the circadian clock, which is a transcriptional mechanism composed of the transcription factors CLOCK and BMAL and their co-repressors, PER and CRY. Nuclear receptors (NRs) represent a large family of hormone-sensitive transcriptional regulators involved in a myriad of biological processes such as development, energy metabolism, reproduction, inflammation, and tissue homeostasis. Recent studies point not only to NR regulation by the clock, but also to NR regulation of the clock itself. Here, we discuss recent studies that functionally and mechanistically implicate NRs as key components of both the universal and adaptive circadian clock mechanisms. As proven pharmacological targets, nuclear receptors are promising targets for therapeutic control of many pathological conditions associated with the disruption of circadian rhythm.
Figures


References
-
- Zhang EE, Kay SA. Clocks not winding down: unravelling circadian networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11:764–776. - PubMed
-
- Debruyne JP, Noton E, Lambert CM, Maywood ES, Weaver DR, Reppert SM. A clock shock: mouse CLOCK is not required for circadian oscillator function. Neuron. 2006;50:465–477. - PubMed
-
- Cheifetz PN. The daily rhythm of the secretion of corticotrophin and corticosterone in rats and mice. J Endocrinol. 1971;49:xi–xii. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL088093/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P42 ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- DK090962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- ES010337/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL105278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK090962/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK057978/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

