pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles employed in controlled drug delivery systems for cancer treatment
- PMID: 24738037
- PMCID: PMC3969802
- DOI: 10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2014.01.003
pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles employed in controlled drug delivery systems for cancer treatment
Abstract
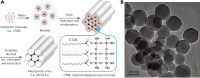
In the fight against cancer, controlled drug delivery systems have emerged to enhance the therapeutic efficacy and safety of anti-cancer drugs. Among these systems, mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) with a functional surface possess obvious advantages and were thus rapidly developed for cancer treatment. Many stimuli-responsive materials, such as nanoparticles, polymers, and inorganic materials, have been applied as caps and gatekeepers to control drug release from MSNs. This review presents an overview of the recent progress in the production of pH-responsive MSNs based on the pH gradient between normal tissues and the tumor microenvironment. Four main categories of gatekeepers can respond to acidic conditions. These categories will be described in detail.
Keywords: Mesoporous silica nanoparticles; antineoplastic protocols; controlled drug release; drug delivery systems; pH-responsive.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest are disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Nazir S, Hussain T, Ayub A, Rashid U, MacRobert AJ. Nanomaterials in combating cancer: therapeutic applications and developments. Nanomedicine 2014;10:19-34 - PubMed
-
- Farokhzad OC, Langer R. Impact of nanotechnology on drug delivery. ACS Nano 2009;3:16-20 - PubMed
-
- Maeda H.The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect in tumor vasculature: the key role of tumor-selective macromolecular drug targeting. Adv Enzyme Regul 2001;41:189-207 - PubMed
-
- Cho K, Wang X, Nie S, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Therapeutic nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:1310-1316 - PubMed
-
- Davis ME, Chen ZG, Shin DM. Nanoparticle therapeutics: an emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2008;7:771-782 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
