Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases: trends in pharmacology and biochemistry
- PMID: 24738050
- PMCID: PMC3971498
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/196754
Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases: trends in pharmacology and biochemistry
Abstract
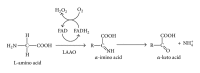
L-amino acid oxidases are enzymes found in several organisms, including venoms of snakes, where they contribute to the toxicity of ophidian envenomation. Their toxicity is primarily due to enzymatic activity, but other mechanisms have been proposed recently which require further investigation. L-amino acid oxidases exert biological and pharmacological effects, including actions on platelet aggregation and the induction of apoptosis, hemorrhage, and cytotoxicity. These proteins present a high biotechnological potential for the development of antimicrobial, antitumor, and antiprotozoan agents. This review provides an overview of the biochemical properties and pharmacological effects of snake venom L-amino acid oxidases, their structure/activity relationship, and supposed mechanisms of action described so far.
Figures
References
-
- Kardong KV. The evolution of the venom apparatus in snakes from Colubrids and Elapids. Memórias do Instituto Butantan. 1982;46:105–118.
-
- Gans C. Reptilian venom: some evolutionary considerations. In: Gans C, Gans KA, editors. Biology of the Reptilia. Vol. 8. London, UK: Academic Press; 1978. pp. 1–42.
-
- Ramos OHP, Selistre-De-Araujo HS. Snake venom metalloproteases—structure and function of catalytic and disintegrin domains. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology C. 2006;142(3-4):328–346. - PubMed
-
- Du X-Y, Clemetson KJ. Snake venom L-amino acid oxidases. Toxicon. 2002;40(6):659–665. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

