Accumulation of heavy metals in crayfish and fish from selected Czech reservoirs
- PMID: 24738051
- PMCID: PMC3971486
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/306103
Accumulation of heavy metals in crayfish and fish from selected Czech reservoirs
Abstract
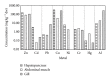
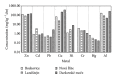
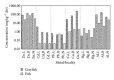
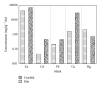
To evaluate the accumulation of aluminium, cadmium, chromium, copper, lead, mercury, nickel, and zinc in crayfish and fish organ tissues, specimens from three drinking water reservoirs (Boskovice, Landštejn, and Nová Říše) and one contaminated site (Darkovské moře) in the Czech Republic were examined. Crayfish hepatopancreas was confirmed to be the primary accumulating site for the majority of metals (Cu > Zn > Ni > Cd > Cr), while Hg and Cr were concentrated in abdominal muscle, and Al and Pb were concentrated in gill. Metals found in Nová Říše specimens included Cu > Zn > Ni and those found in Boskovice included Zn > Hg > Cr. Cd concentrations were observed only in Landštejn specimens, while contaminated Darkovské moře specimens showed the highest levels of accumulation (Cu > Al > Zn > Pb). The majority of evaluated metals were found in higher concentrations in crayfish: Cu > Al > Zn > Ni > Cr > Cd > Pb, with Hg being the only metal accumulating higher in fish. Due to accumulation similarities of Al in crayfish and fish gill, differences of Hg in muscle, and features noted for the remaining metals in examined tissues, biomonitoring should incorporate both crayfish and fish to produce more relevant water quality surveys.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tissue distribution and correlation profiles of heavy-metal accumulation in the freshwater crayfish Astacus leptodactylus.Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2013 May;64(4):676-91. doi: 10.1007/s00244-012-9863-3. Epub 2013 Jan 18. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23329359
-
Correlation profile of the heavy metal distribution in the Pontastacus leptodactylus tissues.An Acad Bras Cienc. 2020;92(2):e20190585. doi: 10.1590/0001-3765202020190585. Epub 2020 Aug 7. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2020. PMID: 32785442
-
Heavy metal accumulation in lake sediments, fish (Oreochromis niloticus and Serranochromis thumbergi), and crayfish (Cherax quadricarinatus) in Lake Itezhi-tezhi and Lake Kariba, Zambia.Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2010 Aug;59(2):291-300. doi: 10.1007/s00244-010-9483-8. Epub 2010 Feb 17. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 20162262
-
Total metal levels in crayfish Astacus leptodactylus (Eschscholtz, 1823), and surface sediments in Lake Terkos, Turkey.Environ Monit Assess. 2010 Oct;169(1-4):385-95. doi: 10.1007/s10661-009-1181-5. Epub 2009 Oct 22. Environ Monit Assess. 2010. PMID: 19847663
-
The use of the red swamp crayfish (Procambarus clarkii, Girard) as indicator of the bioavailability of heavy metals in environmental monitoring in the River Guadiamar (SW, Spain).Sci Total Environ. 2006 Jul 31;366(1):380-90. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.02.023. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Sci Total Environ. 2006. PMID: 16546239
Cited by
-
Bioaccumulation, Biosedimentation, and Health Hazards of Elements in Crayfish, Procambarus clarkii from El-Rahawi Drain and El-Qanatir in the River Nile, Egypt.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023 Jun;201(6):3050-3059. doi: 10.1007/s12011-022-03380-7. Epub 2022 Aug 19. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2023. PMID: 35982260 Free PMC article.
-
Heavy Metals Bioaccumulation in Tissues of Spiny-Cheek Crayfish (Orconectes limosus) from Lake Gopło: Effect of Age and Sex.Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2017 Jun;98(6):740-746. doi: 10.1007/s00128-017-2098-2. Epub 2017 May 5. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28477051 Free PMC article.
-
Combining multivariate analysis and human risk indices for assessing heavy metal contents in muscle tissues of commercially fish from Southern Red Sea, Saudi Arabia.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 Nov;22(21):17012-21. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-4921-9. Epub 2015 Jun 28. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 26122578
-
Evaluation of human health risk assessment of potential toxic metals in commonly consumed crayfish (Palaemon hastatus) in Nigeria.Heliyon. 2019 Dec 27;6(1):e03092. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03092. eCollection 2020 Jan. Heliyon. 2019. PMID: 31909263 Free PMC article.
-
Trace elements in four freshwater fish from a mine-impacted river: spatial distribution, species-specific accumulation, and risk assessment.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Mar;25(9):8861-8870. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1207-z. Epub 2018 Jan 12. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29330818
References
-
- Burger J. Bioindicators: types, development, and use in ecological assessment and research. Environmental Bioindicators. 2006;1(1):22–39.
-
- Besser JM, Brumbaugh WG, May TW, Schmitt CJ. Biomonitoring of lead, zinc, and cadmium in streams draining lead-mining and non-mining areas, Southeast Missouri, USA. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment. 2007;129(1–3):227–241. - PubMed
-
- Morse JC, Bae YJ, Munkhjargal G, et al. Freshwater biomonitoring with macroinvertebrates in East Asia. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment. 2007;5(1):33–42.
-
- Schilderman PAEL, Moonen EJC, Maas LM, Welle I, Kleinjans JCS. Use of crayfish in biomonitoring studies of environmental pollution of the river Meuse. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety. 1999;44(3):241–252. - PubMed
-
- Holdich DM. Distribution of crayfish in Europe and some adjoining countries. Bulletin Francais de la Pêche et de la Pisciculture. 2002;367:611–650.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

