Water-peptide site-specific interactions: a structural study on the hydration of glutathione
- PMID: 24739169
- PMCID: PMC4008841
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2014.01.046
Water-peptide site-specific interactions: a structural study on the hydration of glutathione
Abstract
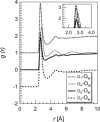
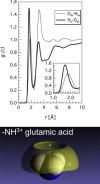
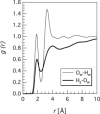
Water-peptide interactions play an important role in determining peptide structure and function. Nevertheless, a microscopic description of these interactions is still incomplete. In this study we have investigated at the atomic scale length the interaction between water and the tripeptide glutathione. The rationale behind this work, based on the combination between a neutron diffraction experiment and a computer simulation, is twofold. It extends previous studies on amino acids, addressing issues such as the perturbation of the water network brought by a larger biomolecule in solution. In addition, and more importantly, it seeks a possible link between the atomic length scale description of the glutathione-water interaction with the specific biological functionality of glutathione, an important intracellular antioxidant. Results indicate a rather weak hydrogen bond between the thiol (-SH) group of cysteine and its first neighbor water molecule. This -SH group serves as a proton donor, is responsible for the biological activity of glutathione, and it is involved in the formation of glutathione disulfide, the oxidized form of glutathione. Moreover, the hydration shell of the chemically identical carboxylate group on the glutamic acid residue and on the glycine residue shows an intriguing different spatial location of water molecules and coordination numbers around the two CO2(-) groups.
Copyright © 2014 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Rupley J.A., Careri G. Protein hydration and function. Adv. Protein Chem. 1991;41:37–172. - PubMed
-
- Ball P. Water as an active constituent in cell biology. Chem. Rev. 2008;108:74–108. - PubMed
-
- Kuhn L.A., Swanson C.A., Getzoff E.D. Atomic and residue hydrophilicity in the context of folded protein structures. Proteins. 1995;23:536–547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

