Heat-induced irreversible denaturation of the camelid single domain VHH antibody is governed by chemical modifications
- PMID: 24739391
- PMCID: PMC4140921
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.534222
Heat-induced irreversible denaturation of the camelid single domain VHH antibody is governed by chemical modifications
Abstract
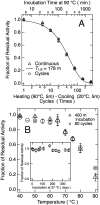
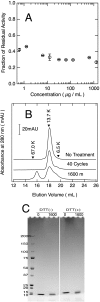
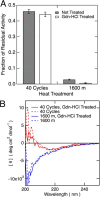
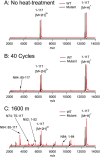
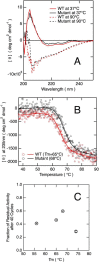
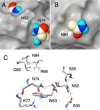
The variable domain of camelid heavy chain antibody (VHH) is highly heat-resistant and is therefore ideal for many applications. Although understanding the process of heat-induced irreversible denaturation is essential to improve the efficacy of VHH, its inactivation mechanism remains unclear. Here, we showed that chemical modifications predominantly governed the irreversible denaturation of VHH at high temperatures. After heat treatment, the activity of VHH was dependent only on the incubation time at 90 °C and was insensitive to the number of heating (90 °C)-cooling (20 °C) cycles, indicating a negligible role for folding/unfolding intermediates on permanent denaturation. The residual activity was independent of concentration; therefore, VHH lost its activity in a unimolecular manner, not by aggregation. A VHH mutant lacking Asn, which is susceptible to chemical modifications, had significantly higher heat resistance than did the wild-type protein, indicating the importance of chemical modifications to VHH denaturation.
Keywords: Antibody; Antibody Engineering; Protein Aggregation; Protein Chemical Modification; Protein Denaturation; Protein Folding; Protein Stability.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures






References
-
- Manning M. C., Chou D. K., Murphy B. M., Payne R. W., Katayama D. S. (2010) Stability of protein pharmaceuticals: an update. Pharm. Res. 27, 544–575 - PubMed
-
- Hamers-Casterman C., Atarhouch T., Muyldermans S., Robinson G., Hamers C., Songa E. B., Bendahman N., Hamers R. (1993) Naturally occurring antibodies devoid of light chains. Nature 363, 446–448 - PubMed
-
- Muyldermans S. (2013) Nanobodies: natural single-domain antibodies. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 82, 775–797 - PubMed
-
- van der Linden R. H., Frenken L. G., de Geus B., Harmsen M. M., Ruuls R. C., Stok W., de Ron L., Wilson S., Davis P., Verrips C. T. (1999) Comparison of physical chemical properties of llama VHH antibody fragments and mouse monoclonal antibodies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1431, 37–46 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

