A multicenter phase I/II study of the BCNU implant (Gliadel(®) Wafer) for Japanese patients with malignant gliomas
- PMID: 24739422
- PMCID: PMC4533485
- DOI: 10.2176/nmc.oa2013-0112
A multicenter phase I/II study of the BCNU implant (Gliadel(®) Wafer) for Japanese patients with malignant gliomas
Abstract
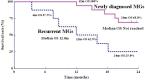
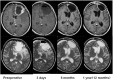
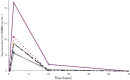
Carmustine (BCNU) implants (Gliadel(®) Wafer, Eisai Inc., New Jersey, USA) for the treatment of malignant gliomas (MGs) were shown to enhance overall survival in comparison to placebo in controlled clinical trials in the United States and Europe. A prospective, multicenter phase I/II study involving Japanese patients with MGs was performed to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics of BCNU implants. The study enrolled 16 patients with newly diagnosed MGs and 8 patients with recurrent MGs. After the insertion of BCNU implants (8 sheets maximum, 61.6 mg BCNU) into the removal cavity, various chemotherapies (including temozolomide) and radiotherapies were applied. After placement, overall and progression-free survival rates and whole blood BCNU levels were evaluated. In patients with newly diagnosed MGs, the overall survival rates at 12 months and 24 months were 100.0% and 68.8%, and the progression-free survival rate at 12 months was 62.5%. In patients with recurrent MGs, the progression-free survival rate at 6 months was 37.5%. There were no grade 4 or higher adverse events noted due to BCNU implants, and grade 3 events were observed in 5 of 24 patients (20.8%). Whole blood BCNU levels reached a peak of 19.4 ng/mL approximately 3 hours after insertion, which was lower than 1/600 of the peak BCNU level recorded after intravenous injections. These levels decreased to less than the detection limit (2.00 ng/mL) after 24 hours. The results of this study involving Japanese patients are comparable to those of previous studies in the United States and Europe.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Tomokazu Aoki is a member of the medical advisory committee of NPC-08 study and received consulting fees from Nobelpharma Co. Ltd. and an honoraria for speaking from Eisai Co. Ltd. Dr. Ryo Nishikawa is a member of the medical advisory committee of NPC-08 study and received consulting fees from Nobelpharma Co. Ltd. Dr. Nishikawa is also a member of the Avaglio study steering committee (funded by F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Ltd) and has received research funding and speaking fees from MSD KK as well as honoraria for speaking from Eisai Co. Ltd. Dr. Kazuhiko Sugiyama is a member of the medical advisory committee of NPC-08 study and received consulting fees from Nobelpharma Co. Ltd. and honoraria for speaking from Eisai Co. Ltd. Dr. Masao Matsutani is a coordinating investigator of NPC-08 study, a member of the advisory committee of MSD KK, and a coordinating investigator for Chugai Pharmaceutical Co. Ltd. Dr. Matsutani also received consulting fees from Nobelpharma Co. Ltd.
The authors declare no other conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Committee of Brain Tumor Registry of Japan : Report of brain tumor registry of Japan (1984–2000), ed 12 . Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 49( Suppl): S1– S96, 2009. - PubMed
-
- Brem H, Piantadosi S, Burger PC, Walker M, Selker R, Vick NA, Black K, Sisti M, Brem S, Mohr G: Placebo-controlled trial of safety and efficacy of intraoperative controlled delivery by biodegradable polymers of chemotherapy for recurrent gliomas. The Polymer-brain Tumor Treatment Group. Lancet 345: 1008– 1012, 1995. - PubMed
-
- Valtonen S, Timonen U, Toivanen P, Kalimo H, Kivipelto L, Heiskanen O, Unsgaard G, Kuurne T: Interstitial chemotherapy with carmustine-loaded polymers for high-grade gliomas: a randomized double-blind study. Neurosurgery 41: 44– 48; discussion 48–49, 1997. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology-v.1, 2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

