Importance of N-glycosylation on CD147 for its biological functions
- PMID: 24739808
- PMCID: PMC4013633
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms15046356
Importance of N-glycosylation on CD147 for its biological functions
Abstract
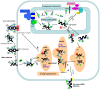
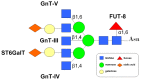
Glycosylation of glycoproteins is one of many molecular changes that accompany malignant transformation. Post-translational modifications of proteins are closely associated with the adhesion, invasion, and metastasis of tumor cells. CD147, a tumor-associated antigen that is highly expressed on the cell surface of various tumors, is a potential target for cancer diagnosis and therapy. A significant biochemical property of CD147 is its high level of glycosylation. Studies on the structure and function of CD147 glycosylation provide valuable clues to the development of targeted therapies for cancer. Here, we review current understanding of the glycosylation characteristics of CD147 and the glycosyltransferases involved in the biosynthesis of CD147 N-glycans. Finally, we discuss proteins regulating CD147 glycosylation and the biological functions of CD147 glycosylation.
Figures

References
-
- Biswas C. Tumor cell stimulation of collagenase production by fibroblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1982;109:1026–1034. - PubMed
-
- Gabison E.E., Hoang-Xuan T., Mauviel A., Menashi S. EMMPRIN/CD147, an MMP modulator in cancer, development and tissue repair. Biochimie. 2005;87:361–368. - PubMed
-
- Schmidt R., Bültmann A., Fischel S., Gillitzer A., Cullen P., Walch A., Jost P., Ungerer M., Tolley N.D., Lindemann S., et al. Extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer (CD147) is a novel receptor on platelets, activates platelets, and augments nuclear factor {kappa}B dependent inflammation in monocytes. Circ. Res. 2008;102:302–309. - PubMed
-
- Ruiz S., Castro A., Bustelo X.R. CD147 inhibits the nuclear factor of activated T-cells by impairing vav1 and rac1 downstream signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2008;283:5554–5566. - PubMed
-
- Biswas C., Zhang Y., DeCastro R., Guo H., Nakamura T., Kataoka H., Nabeshima K. The human tumor cell-derived collagenase stimulatory factory factor (renamed EMMPRIN) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cancer. Res. 1995;55:434–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

