Chemical modulation of the biological activity of reutericyclin: a membrane-active antibiotic from Lactobacillus reuteri
- PMID: 24739957
- PMCID: PMC4894453
- DOI: 10.1038/srep04721
Chemical modulation of the biological activity of reutericyclin: a membrane-active antibiotic from Lactobacillus reuteri
Abstract
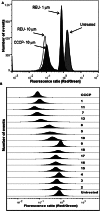
Whilst the development of membrane-active antibiotics is now an attractive therapeutic concept, progress in this area is disadvantaged by poor knowledge of the structure-activity relationship (SAR) required for optimizing molecules to selectively target bacteria. This prompted us to explore the SAR of the Lactobacillus reuteri membrane-active antibiotic reutericyclin, modifying three key positions about its tetramic acid core. The SAR revealed that lipophilic analogs were generally more active against Gram-positive pathogens, but introduction of polar and charged substituents diminished their activity. This was confirmed by cytometric assays showing that inactive compounds failed to dissipate the membrane potential. Radiolabeled substrate assays indicated that dissipation of the membrane potential by active reutericyclins correlated with inhibition of macromolecular synthesis in cells. However, compounds with good antibacterial activities also showed cytotoxicity against Vero cells and hemolytic activity. Although this study highlights the challenge of optimizing membrane-active antibiotics, it shows that by increasing antibacterial potency the selectivity index could be widened, allowing use of lower non-cytotoxic doses.
Figures

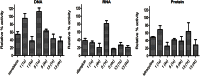
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

