Oncogene-like induction of cellular invasion from centrosome amplification
- PMID: 24739973
- PMCID: PMC4061398
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13277
Oncogene-like induction of cellular invasion from centrosome amplification
Abstract
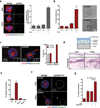
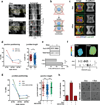
Centrosome amplification has long been recognized as a feature of human tumours; however, its role in tumorigenesis remains unclear. Centrosome amplification is poorly tolerated by non-transformed cells and, in the absence of selection, extra centrosomes are spontaneously lost. Thus, the high frequency of centrosome amplification, particularly in more aggressive tumours, raises the possibility that extra centrosomes could, in some contexts, confer advantageous characteristics that promote tumour progression. Using a three-dimensional model system and other approaches to culture human mammary epithelial cells, we find that centrosome amplification triggers cell invasion. This invasive behaviour is similar to that induced by overexpression of the breast cancer oncogene ERBB2 (ref. 4) and indeed enhances invasiveness triggered by ERBB2. Our data indicate that, through increased centrosomal microtubule nucleation, centrosome amplification increases Rac1 activity, which disrupts normal cell-cell adhesion and promotes invasion. These findings demonstrate that centrosome amplification, a structural alteration of the cytoskeleton, can promote features of malignant transformation.
Figures

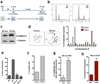

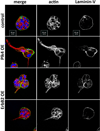




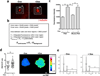
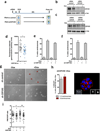


References
Supplementary References
-
- Debnath J, et al. The role of apoptosis in creating and maintaining luminal space within normal and oncogene-expressing mammary acini. Cell. 2002;111:29–40. - PubMed
-
- Xiang B, Muthuswamy SK. Using three-dimensional acinar structures for molecular and cell biological assays. Methods Enzymol. 2006;406:692–701. - PubMed
-
- Paszek MJ, Weaver VM. The tension mounts: mechanics meets morphogenesis and malignancy. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2004;9:325–342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

