Myeloid-specific Rictor deletion induces M1 macrophage polarization and potentiates in vivo pro-inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 24740015
- PMCID: PMC3989321
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095432
Myeloid-specific Rictor deletion induces M1 macrophage polarization and potentiates in vivo pro-inflammatory response to lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
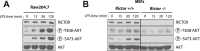
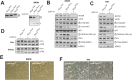
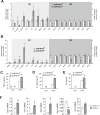
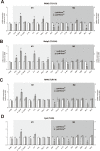
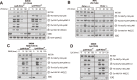
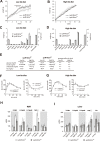
The phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) axis plays a central role in attenuating inflammation upon macrophage stimulation with toll-like receptor (TLR) ligands. The mechanistic target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) relays signal from PI3K to Akt but its role in modulating inflammation in vivo has never been investigated. To evaluate the role of mTORC2 in the regulation of inflammation in vivo, we have generated a mouse model lacking Rictor, an essential mTORC2 component, in myeloid cells. Primary macrophages isolated from myeloid-specific Rictor null mice exhibited an exaggerated response to TLRs ligands, and expressed high levels of M1 genes and lower levels of M2 markers. To determine whether the loss of Rictor similarly affected inflammation in vivo, mice were either fed a high fat diet, a situation promoting chronic but low-grade inflammation, or were injected with lipopolysaccharide (LPS), which mimics an acute, severe septic inflammatory condition. Although high fat feeding contributed to promote obesity, inflammation, macrophage infiltration in adipose tissue and systemic insulin resistance, we did not observe a significant impact of Rictor loss on these parameters. However, mice lacking Rictor exhibited a higher sensitivity to septic shock when injected with LPS. Altogether, these results indicate that mTORC2 is a key negative regulator of macrophages TLR signalling and that its role in modulating inflammation is particularly important in the context of severe inflammatory challenges. These observations suggest that approaches aimed at modulating mTORC2 activity may represent a possible therapeutic approach for diseases linked to excessive inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Adipose tissue mTORC2 regulates ChREBP-driven de novo lipogenesis and hepatic glucose metabolism.Nat Commun. 2016 Apr 21;7:11365. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11365. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27098609 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2) negatively regulates Toll-like receptor 4-mediated inflammatory response via FoxO1.J Biol Chem. 2011 Dec 30;286(52):44295-305. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.258053. Epub 2011 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 22045807 Free PMC article.
-
Rictor in perivascular adipose tissue controls vascular function by regulating inflammatory molecule expression.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013 Sep;33(9):2105-11. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.301001. Epub 2013 Jul 18. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013. PMID: 23868942
-
Unmasking the impact of Rictor in cancer: novel insights of mTORC2 complex.Carcinogenesis. 2018 Jul 30;39(8):971-980. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgy086. Carcinogenesis. 2018. PMID: 29955840 Review.
-
The role of RICTOR downstream of receptor tyrosine kinase in cancers.Mol Cancer. 2018 Feb 19;17(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12943-018-0794-0. Mol Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29455662 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolic Reprogramming Mediated by the mTORC2-IRF4 Signaling Axis Is Essential for Macrophage Alternative Activation.Immunity. 2016 Oct 18;45(4):817-830. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.09.016. Immunity. 2016. PMID: 27760338 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage Apoptosis and Efferocytosis in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis.Circ J. 2016 Oct 25;80(11):2259-2268. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-16-0924. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Circ J. 2016. PMID: 27725526 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of alterations in macrophage activation associated with disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 18;13(12):e0208132. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0208132. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30562343 Free PMC article.
-
Next Generation Strategies for Geroprotection via mTORC1 Inhibition.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020 Jan 1;75(1):14-23. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glz056. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 30794726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Complexity of Targeting PI3K-Akt-mTOR Signalling in Human Acute Myeloid Leukaemia: The Importance of Leukemic Cell Heterogeneity, Neighbouring Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Immunocompetent Cells.Molecules. 2016 Nov 11;21(11):1512. doi: 10.3390/molecules21111512. Molecules. 2016. PMID: 27845732 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gordon S (2003) Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol 3: 23–35. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nat Immunol 11: 373–384. - PubMed
-
- Olefsky JM, Glass CK (2010) Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 72: 219–246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

