TFPI cofactor function of protein S: essential role of the protein S SHBG-like domain
- PMID: 24740810
- PMCID: PMC4064334
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2014-01-551812
TFPI cofactor function of protein S: essential role of the protein S SHBG-like domain
Abstract
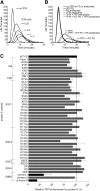
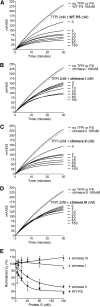
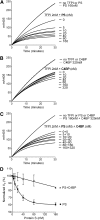
Protein S is a cofactor for tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI), accelerating the inhibition of activated factor X (FXa). TFPI Kunitz domain 3 residue Glu226 is essential for enhancement of TFPI by protein S. To investigate the complementary functional interaction site on protein S, we screened 44 protein S point, composite or domain swap variants spanning the whole protein S molecule for their TFPI cofactor function using a thrombin generation assay. Of these variants, two protein S/growth arrest-specific 6 chimeras, with either the whole sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG)-like domain (Val243-Ser635; chimera III) or the SHBG laminin G-type 1 subunit (Ser283-Val459; chimera I), respectively, substituted by the corresponding domain in growth arrest-specific 6, were unable to enhance TFPI. The importance of the protein S SHBG-like domain (and its laminin G-type 1 subunit) for binding and enhancement of TFPI was confirmed in FXa inhibition assays and using surface plasmon resonance. In addition, protein S bound to C4b binding protein showed greatly reduced enhancement of TFPI-mediated inhibition of FXa compared with free protein S. We show that binding of TFPI to the protein S SHBG-like domain enables TFPI to interact optimally with FXa on a phospholipid membrane.
© 2014 by The American Society of Hematology.
Figures



References
-
- Wun TC, Kretzmer KK, Girard TJ, Miletich JP, Broze GJ., Jr Cloning and characterization of a cDNA coding for the lipoprotein-associated coagulation inhibitor shows that it consists of three tandem Kunitz-type inhibitory domains. J Biol Chem. 1988;263(13):6001–6004. - PubMed
-
- Dahm A, Van Hylckama Vlieg A, Bendz B, Rosendaal F, Bertina RM, Sandset PM. Low levels of tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) increase the risk of venous thrombosis. Blood. 2003;101(11):4387–4392. - PubMed
-
- Broze GJ, Jr, Lange GW, Duffin KL, MacPhail L. Heterogeneity of plasma tissue factor pathway inhibitor. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1994;5(4):551–559. - PubMed
-
- Nordfang O, Bjørn SE, Valentin S, et al. The C-terminus of tissue factor pathway inhibitor is essential to its anticoagulant activity. Biochemistry. 1991;30(43):10371–10376. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

