Medial vascular calcification revisited: review and perspectives
- PMID: 24740885
- PMCID: PMC4072893
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehu163
Medial vascular calcification revisited: review and perspectives
Abstract
Vascular calcifications (VCs) are actively regulated biological processes associated with crystallization of hydroxyapatite in the extracellular matrix and in cells of the media (VCm) or intima (VCi) of the arterial wall. Both patterns of VC often coincide and occur in patients with type II diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and other less frequent disorders; VCs are also typical in senile degeneration. In this article, we review the current state of knowledge about the pathology, molecular biology, and nosology of VCm, expand on potential mechanisms responsible for poor prognosis, and expose some of the directions for future research in this area.
Keywords: Mönckeberg's media sclerosis; Vascular calcifications; Vascular function; Vascular molecular biology and genetics.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2014. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

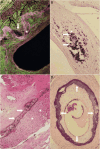


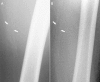
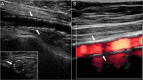
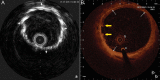
References
-
- Schlieper G, Aretz A, Verberckmoes SC, Krüger T, Behets GJ, Ghadimi R, Weinrich TE, Rohrmann D, Langer S, Tordoir JH, Amann K, Westenfeld R, Brandenburg VM, D'Haese PC, Mayer J, Ketteler M, McKee MD, Floege J. Ultrastructural analysis of vascular calcifications in uremia. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2010;21:689–696. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shanahan CM. Inflammation ushers in calcification: a cycle of damage and protection? Circulation. 2007;116:2782–2785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

