Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of N-acetyl cysteine in carbamazepine-administered rats
- PMID: 24741196
- PMCID: PMC3987193
- DOI: 10.4103/0253-7613.129321
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant activity of N-acetyl cysteine in carbamazepine-administered rats
Abstract
Objectives: The present study evaluates the hepatoprotective activity of N-acetyl cysteine (NAC) against carbamazepine (CBZ)-induced hepatotoxicity.
Materials and methods: Rats were treated with CBZ (50 mg/kg p.o.) and CBZ supplemented with NAC 50, 100 and 200 mg/kg for 45 days, after which blood samples were collected and subjected to liver function tests. Animals were killed, liver was separated, weighed and the levels of antioxidants and liver enzymes were estimated. In addition, histopathological investigation was also performed.
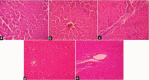
Results: Serum glutamate pyruvate transaminase (SGPT), serum glutamate oxaloacetate (SGOT) transaminase, alkaline phosphatase (ALP), bilirubin, lipid peroxidation, absolute and relative liver weights were significantly (P < 0.05) elevated, whereas serum levels of albumin, total protein and body weight were decreased in the CBZ-treated animals. CBZ also produced vacuolar degeneration, centrilobular congestion and hepatic necrosis as evidenced from histopathological report. NAC significantly reduced the levels of serum transaminase, ALP, bilirubin and liver weight and increased the levels of total protein, albumin and body weight.
Conclusion: It was observed that NAC increased the glutathione (GSH) content, reduced lipid peroxidation and reversed the CBZ-induced histopathological abnormalities. CBZ-induced hepatotoxicity may be due its toxic epoxide metabolite-induced oxidative stress.
Keywords: Carbamazepine; N-acetyl cysteine; hepatotoxicity; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Wyllie E, Wyllie R. Routine laboratory monitoring for serious adverse effects of antiepileptic medications: The controversy. Epilepsia. 1991;32:S74–9. - PubMed
-
- Bernus I, Dickinson RG, Hooper WD, Eadie MJ. Dose-dependent metabolism of carbamazepine in humans. Epilepsy Res. 1996;24:163–72. - PubMed
-
- Scheyer RD, Cramer JA, Mattson RH. A pharmacodynamic approach to the estimate of carbamazepine autoinduction. J Pharm Sci. 1994;83:491–4. - PubMed
-
- Benedetti MS, Ruty B, Baltes E. Induction of endogenous pathways by antiepileptics and clinical implications. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2005;19:511–29. - PubMed
-
- Driefus FE, Langer DH. Hepatic considerations in the use of antiepileptic drugs. Epilepsia. 1987;28:S23–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical