Positive effects of a novel non-peptidyl low molecular weight radical scavenger in renal ischemia/reperfusion: a preliminary report
- PMID: 24741476
- PMCID: PMC3979974
- DOI: 10.1186/2193-1801-3-158
Positive effects of a novel non-peptidyl low molecular weight radical scavenger in renal ischemia/reperfusion: a preliminary report
Abstract
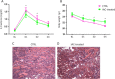
Ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) is one of the most common causes of acute kidney injury. Reactive oxygen species have been recognized to be an important contributor to the pathogenesis of I/R injury. We hypothesize that a non-peptidyl low molecular weight radical scavenger (IAC) therapy may counteract this factor, ultimately providing some protection after acute phase renal I/R injury. The aim of this preliminary study was to assess the ability of IAC to reduce acute kidney injury in C57BL/6 mice after 30-minute of bilateral ischemia followed by reperfusion. The rise in serum creatinine level was higher in C57BL/6 control mice after I/R when compared to IAC (1 mg)-treated mice. Control mice showed greater body weight loss compared to IAC-treated mice, and at pathology, reduced signs of tubular necrosis were also evident in IAC-treated mice. These preliminary evidences lay the basis for more comprehensive studies on the positive effects of IAC as a complementary therapeutic approach for acute phase renal I/R injury.
Keywords: Inflammation; Ischemia/reperfusion; Kidney disease; Kidney transplantation; Radical oxygen species.
Figures
References
-
- D'Aleo V, Del Guerra S, Martano M, Bonamassa B, Canistro D, Soleti A, Valgimigli L, Paolini M, Filipponi F, Boggi U, Del Prato S, Lupi R. The non-peptidyl low molecular weight radical scavenger IAC protects human pancreatic islets from lipotoxicity. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2009;309:63–6. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.05.010. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fiorina P, Venturini M, Folli F, Losio C, Maffi P, Placidi C, La Rosa S, Orsenigo E, Socci C, Capella C, Del Maschio A, Secchi A. Natural history of kidney graft survival, hypertrophy, and vascular function in end-stage renal disease type 1 diabetic kidney-transplanted patients: beneficial impact of pancreas and successful islet cotransplantation. Diabetes Care. 2005;28:1303–10. doi: 10.2337/diacare.28.6.1303. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

