Congenital hypothyroidism in neonates
- PMID: 24741519
- PMCID: PMC3987273
- DOI: 10.4103/2230-8210.129114
Congenital hypothyroidism in neonates
Abstract
Context: Congenital hypothyroidism (CH) is one of the most common preventable causes of mental retardation in children and it occurs in approximately 1:2,000-1:4,000 newborns.
Aims and objectives: The aim of this study is to determine the frequency of CH in neonates.
Settings and design: This cross-sectional study was conducted in neonatal units of the Department of Pediatrics Unit-I, King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital, Lahore and Lady Willington Hospital Lahore in 6 months (January-June 2011).
Materials and methods: Sample was collected by non-probability purposive sampling. After consent, 550 newborn were registered for the study. Demographic data and relevant history was recorded. After aseptic measures, 2-3 ml venous blood analyzed for thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) level by immunoradiometric assay. Treatment was started according to the individual merit as per protocol.
Statistical analysis used: Data was analyzed by SPSS 17 and Chi-square test was applied to find out the association of CH with different variables.
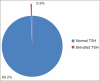
Results: The study population consisted of 550 newborns. Among 550 newborns, 4 (0.8%) newborns had elevated TSH level. CH had statistically significant association with mother's hypothyroidism (P value 0.000) and mother's drug intake during the pregnancy period (P value 0.013).
Conclusion: CH is 0.8% in neonates. It has statistically significant association with mother's hypothyroidism and mother's drug intake during pregnancy.
Keywords: Congenital hypothyroidism; newborn; thyroid-stimulating hormone.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Bernal J. Action of thyroid hormone in brain. J Endocrinol Invest. 2002;25:268–88. - PubMed
-
- Büyükgebiz A. Newborn screening for congenital hypothyroidism. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2006;19:1291–8. - PubMed
-
- Klein AH, Agustin AV, Foley TP., Jr Successful laboratory screening for congenital hypothyroidism. Lancet. 1974;2:77–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources