Ca²⁺-regulated secretory granule exocytosis in pancreatic and parotid acinar cells
- PMID: 24742357
- PMCID: PMC4058401
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ceca.2014.03.003
Ca²⁺-regulated secretory granule exocytosis in pancreatic and parotid acinar cells
Abstract
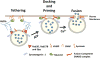
Protein secretion from acinar cells of the pancreas and parotid glands is controlled by G-protein coupled receptor activation and generation of the cellular messengers Ca(2+), diacylglycerol and cAMP. Secretory granule (SG) exocytosis shares some common characteristics with nerve, neuroendocrine and endocrine cells which are regulated mainly by elevated cell Ca(2+). However, in addition to diverse signaling pathways, acinar cells have large ∼1 μm diameter SGs (∼30 fold larger diameter than synaptic vesicles), respond to stimulation at slower rates (seconds versus milliseconds), demonstrate significant constitutive secretion, and in isolated acini, undergo sequential compound SG-SG exocytosis at the apical membrane. Exocytosis proceeds as an initial rapid phase that peaks and declines over 3 min followed by a prolonged phase that decays to near basal levels over 20-30 min. Studies indicate the early phase is triggered by Ca(2+) and involves the SG proteins VAMP2 (vesicle associated membrane protein2), Ca(2+)-sensing protein synatotagmin 1 (syt1) and the accessory protein complexin 2. The molecular details for regulation of VAMP8-mediated SG exocytosis and the prolonged phase of secretion are still emerging. Here we review the known regulatory molecules that impact the sequential exocytic process of SG tethering, docking, priming and fusion in acinar cells.
Keywords: Acinar exocytosis; Ca(2+); Complexin; Docking; Fusion; Membrane trafficking; Pancreatic parotid acinar secretion; SNARE; Secretory granules; Synaptotagmin; Tethering; Zymogen granules; cAMP.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- de Pont JJ, Fleuren-Jakobs AM. Synergistic effect of A23187 and a phorbol ester on amylase secretion from rabbit pancreatic acini. FEBS letters. 1984;170:64–68. - PubMed
-
- Collen MJ, Sutliff VE, Pan GZ, Gardner JD. Postreceptor modulation of action of VIP and secretin on pancreatic enzyme secretion by secretagogues that mobilize cellular calcium. The American journal of physiology. 1982;242:G423–428. - PubMed
-
- Quissell DO, Watson E, Dowd FJ. Signal transduction mechanisms involved in salivary gland regulated exocytosis. Critical reviews in oral biology and medicine : an official publication of the American Association of Oral Biologists. 1992;3:83–107. - PubMed
-
- Scott J, Baum BJ. Involvement of cyclic AMP and calcium in exocrine protein secretion induced by vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in rat parotid cells. Biochimica et biophysica acta. 1985;847:255–262. - PubMed
-
- Verhage M, Sorensen JB. Vesicle docking in regulated exocytosis. Traffic. 2008;9:1414–1424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

