A p38 substrate-specific MK2-EGFP translocation assay for identification and validation of new p38 inhibitors in living cells: a comprising alternative for acquisition of cellular p38 inhibition data
- PMID: 24743242
- PMCID: PMC3990705
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095641
A p38 substrate-specific MK2-EGFP translocation assay for identification and validation of new p38 inhibitors in living cells: a comprising alternative for acquisition of cellular p38 inhibition data
Abstract
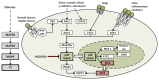
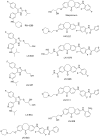
The fundamental role of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) in inflammation underlines their importance as therapeutic targets for various inflammatory medical conditions, including infectious, vascular, neurobiological and autoimmune disease. Although decades of research have yielded several p38 inhibitors, most clinical trials have failed, due to lack of selectivity and efficacy in vivo. This underlines the continuous need to screen for novel structures and chemotypes of p38 inhibitors. Here we report an optimized MK2-EGFP translocation assay in a semi-automated image based High Content Analysis (HCA) system to screen a combinatorial library of 3362 proprietary compounds with extensive variations of chemotypes. By determining the levels of redistribution of MK2-EGFP upon activation of the Rac/p38 pathway in combination with compound treatment, new candidates were identified, which modulate p38 activity in living cells. Based on integrated analysis of TNFα release from human whole blood, biochemical kinase activity assays and JNK3 selectivity testing, we show that this cell based assay reveals a high overlap and predictability for cellular efficacy, selectivity and potency of tested compounds. As a result we disclose a new comprehensive short-list of subtype inhibitors which are functional in the low nanomolar range and might provide the basis for further lead-optimization. In accordance to previous reports, we demonstrate that the MK2-EGFP translocation assay is a suitable primary screening approach for p38-MAPK drug development and provide an attractive labor- and cost saving alternative to other cell based methods including determination of cytokine release from hPBMCs or whole blood.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
From Enzyme to Whole Blood: Sequential Screening Procedure for Identification and Evaluation of p38 MAPK Inhibitors.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1360:123-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3073-9_10. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26501907
-
Generation and characterization of a stable MK2-EGFP cell line and subsequent development of a high-content imaging assay on the Cellomics ArrayScan platform to screen for p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors.Methods Enzymol. 2006;414:364-89. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)14021-5. Methods Enzymol. 2006. PMID: 17110203
-
Assay development and case history of a 32K-biased library high-content MK2-EGFP translocation screen to identify p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitors on the ArrayScan 3.1 imaging platform.Methods Enzymol. 2006;414:419-39. doi: 10.1016/S0076-6879(06)14023-9. Methods Enzymol. 2006. PMID: 17110205
-
Biological functions and role of mitogen-activated protein kinase activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) in inflammatory diseases.Pharmacol Rep. 2017 Aug;69(4):746-756. doi: 10.1016/j.pharep.2017.03.023. Epub 2017 Apr 8. Pharmacol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28582691 Review.
-
MK2: a novel molecular target for anti-inflammatory therapy.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008 Aug;12(8):921-36. doi: 10.1517/14728222.12.8.921. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2008. PMID: 18620516 Review.
Cited by
-
In silico insights into prediction and analysis of potential novel pyrrolopyridine analogs against human MAPKAPK-2: a new SAR-based hierarchical clustering approach.3 Biotech. 2018 Sep;8(9):385. doi: 10.1007/s13205-018-1405-x. Epub 2018 Aug 23. 3 Biotech. 2018. PMID: 30148035 Free PMC article.
-
Live-cell measurements of kinase activity in single cells using translocation reporters.Nat Protoc. 2018 Jan;13(1):155-169. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2017.128. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Nat Protoc. 2018. PMID: 29266096
-
The food dye Tartrazine disrupts vascular formation both in zebrafish larvae and in human primary endothelial cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 5;14(1):30367. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82076-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39639097 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kumar S, Boehm J, Lee JC (2003) p38 MAP kinases: key signalling molecules as therapeutic targets for inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2: 717–726. - PubMed
-
- Cuenda A, Rousseau S (2007) p38 MAP-kinases pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1773: 1358–1375. - PubMed
-
- Herlaar E, Brown Z (1999) p38 MAPK signalling cascades in inflammatory disease. Mol Med Today 5: 439–447. - PubMed
-
- Ono K, Han J (2000) The p38 signal transduction pathway: activation and function. Cell Signal 12: 1–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

