Anti-inflammatory effects of high-density lipoprotein through activating transcription factor 3: benefit beyond cholesterol transport-dependent processes
- PMID: 24743432
- PMCID: PMC4118762
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.114.303553
Anti-inflammatory effects of high-density lipoprotein through activating transcription factor 3: benefit beyond cholesterol transport-dependent processes
Keywords: HDL cholesterol; commentary; inflammation.
Figures
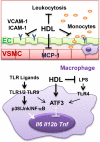
Comment on
-
High-density lipoprotein mediates anti-inflammatory reprogramming of macrophages via the transcriptional regulator ATF3.Nat Immunol. 2014 Feb;15(2):152-60. doi: 10.1038/ni.2784. Epub 2013 Dec 8. Nat Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24317040 Free PMC article.
References
-
- De Nardo D, Labzin LI, Kono H, Seki R, Schmidt SV, Beyer M, Xu D, Zimmer S, Lahrmann C, Schildberg FA, Vogelhuber J, Kraut M, Ulas T, Kerksiek A, Krebs W, Bode N, Grebe A, Fitzgerald ML, Hernandez NJ, Williams BR, Knolle P, Kneilling M, Rocken M, Lutjohann D, Wright SD, Schultze JL, Latz E. High-density lipoprotein mediates anti-inflammatory reprogramming of macrophages via the transcriptional regulator atf3. Nature immunology. 2014;15:152–160. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Xia P, Vadas MA, Rye KA, Barter PJ, Gamble JR. High density lipoproteins (hdl) interrupt the sphingosine kinase signaling pathway. A possible mechanism for protection against atherosclerosis by hdl. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1999;274:33143–33147. - PubMed
-
- Murphy AJ, Woollard KJ, Hoang A, Mukhamedova N, Stirzaker RA, McCormick SP, Remaley AT, Sviridov D, Chin-Dusting J. High-density lipoprotein reduces the human monocyte inflammatory response. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2008;28:2071–2077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

