Management of the complications of BPH/BOO
- PMID: 24744522
- PMCID: PMC3989825
- DOI: 10.4103/0970-1591.127856
Management of the complications of BPH/BOO
Abstract
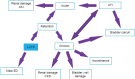
Most men will develop histological BPH if they live long enough. Approximately, half will develop benign prostatic enlargement (BPE) and about half of these will get BOO with high bladder pressures and low flow, this in turn leads to detrusor wall hypertrophy. Many of these men will only have lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) but a significant number will also suffer the other complications of BPH. These include urinary retention (acute and chronic), haematuria, urinary tract infection, bladder stones, bladder wall damage, renal dysfunction, incontinence and erectile dysfunction. Recognition of the complications of BPH/BOO early allows more effective management of these complications. This is particularly important for the more serious urinary infections and also for high-pressure chronic retention (HPCR). Complications of LUTS/BPH are very rare in clinical trials because of their strict inclusion and exclusion criteria but are more common in real life practice.
Keywords: Bladder calculi; renal dysfunction; urinary retention; urinary tract infection.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Speakman M. Lower urinary tract symptoms suggestive of benign prostatic hyperplasia (LUTS/BPH): More than treating symptoms? Eur Urol Suppl. 2008;7:680–9.
-
- McConnell JD, Roehrborn CG, Bautista OM, Andriole GL, Jr, Dixon CM, Kusek JW, et al. The long-term effect of doxazosin, finasteride, and combination therapy on the clinical progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia. N Engl J Med. 2003;349:2387–98. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick J, Kirby R. Management of acute urinary retention. BJU Int. 2006;97(Suppl 2):16–20. - PubMed
-
- Thomas K, Oades G, Taylor-Hay C, Kirby RS. Acute urinary retention: What is the impact on patients’ quality of life? BJU Int. 2005;95:72–6. - PubMed
-
- The Standardisation of lower urinary tract function. [Last accessed on 2013 Nov 1]. Available from: http://www.ics.org/Documents/DocumentsDownload.aspx?DocumentID=22 .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

