Differential role of CSF alpha-synuclein species, tau, and Aβ42 in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 24744728
- PMCID: PMC3978246
- DOI: 10.3389/fnagi.2014.00053
Differential role of CSF alpha-synuclein species, tau, and Aβ42 in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
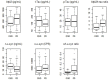
There is a great interest in developing cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of Parkinson's disease (PD). CSF alpha synuclein (α-syn) species, namely total and oligomeric α-syn (t-α-syn and o-α-syn), have shown to be of help for PD diagnosis. Preliminary evidences show that the combination of CSF t-α-syn and classical Alzheimer's disease (AD) biomarkers-β-amyloid 1-42 (Aβ42), total tau (t-tau), phosphorylated tau (p-tau)-differentiate PD patients from controls, and that reduced levels of Aβ42 represent a predictive factor for development of cognitive deterioration in PD. In this prospective study carried out in 44 PD patients and 25 neurological controls we wanted to verify whether the combination of CSF α-synuclein species-t-α-syn and o-α-syn-and classical AD biomarkers may help in differentiating PD from neurological controls, and if these biomarkers may predict cognitive decline. The median of follow-up duration was 3 years (range: 2-6 years). Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE) and Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) were used for monitoring cognitive changes along time, being administered once a year. Oligo/total α-syn ratio (o/t-α-syn ratio) confirmed its diagnostic value, significantly contributing to the discrimination of PD from neurological controls. A greater diagnostic accuracy was reached when combining o/t-α-syn and Aβ42/tau ratios (Sens = 0.70, Spec = 0.84, AUC = 0.82; PPV = 0.89, NPV = 0.62, LR+ = 4.40, DOR = 12.52). Low CSF Aβ42 level was associated with a higher rate of MMSE and MoCA decline, confirming its role as independent predictive factor for cognitive decline in PD. None of the other biomarkers assessed (t-tau, p-tau, t-α-syn and o-α-syn) showed to have prognostic value. We conclude that combination of CSF o/t-α-syn and Aβ42/tau ratios improve the diagnostic accuracy of PD. PD patients showing low CSF Aβ42 levels at baseline are more prone to develop cognitive decline.
Keywords: Aβ42; Parkinson's disease; alpha synuclein; cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers; cognitive decline; phosphorylated tau; total tau.
Figures

References
-
- Alves G., Brønnick K., Aarsland D., Blennow K., Zetterberg H., Ballard C., et al. (2010). CSF amyloid-beta and tau proteins, and cognitive performance, in early and untreated Parkinson's disease: the Norwegian ParkWest study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 81, 1080–1086 10.1136/jnnp.2009.199950 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

