Effectiveness of Stimulation of Acupoint KI 1 by Artemisia vulgaris (Moxa) for the Treatment of Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 24744807
- PMCID: PMC3972940
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/187484
Effectiveness of Stimulation of Acupoint KI 1 by Artemisia vulgaris (Moxa) for the Treatment of Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Objective. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials has been performed to assess the effectiveness of stimulation of acupoint KI 1 by Artemisia vulgaris (the Japanese name is moxa) to lower blood pressure compared to antihypertensive drugs. Methods and Findings. Articles published from 1980 to August 2013 in databases of CENTRAL, Pubmed, CBM, CNKI, VIP, and online clinical trial registry websites were searched. Studies included were randomized controlled trials (RCTs); moxibustion-type intervention on KI 1 compared with antihypertensive drugs; meta-analysis showed superior effects of moxibustion plus antihypertensive drugs on systolic blood pressure (WMD: -4.91 [-7.54, -2.28]; P = 0.0003) but no superior effects on diastolic blood pressure (WMD: -6.38 [-17.17, 4.41]; P = 0.25). Conclusions. Our systematic review of the current literature shows a beneficial effect of using moxibustion interventions on KI 1 to lower blood pressure compared to antihypertensive drugs. However, the results are influenced by the existing differences in design of the current trials.
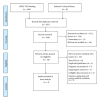
Figures


Similar articles
-
Is it a new approach for treating senile hypertension with kidney-tonifying chinese herbal formula? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014;2014:473038. doi: 10.1155/2014/473038. Epub 2014 Feb 17. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014. PMID: 24693323 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative effects of artemisia vulgaris and charcoal moxa stimulating Zhongwan (CV 12) on body temperature in healthy participants: a cross-over single-blind randomized study.J Tradit Chin Med. 2015 Oct;35(5):551-7. doi: 10.1016/s0254-6272(15)30138-2. J Tradit Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26591685 Clinical Trial.
-
Chinese herbal medicine qi ju di huang wan for the treatment of essential hypertension: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:262685. doi: 10.1155/2013/262685. Epub 2013 Jun 25. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013. PMID: 23878593 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of moxibustion or acupoint therapy for the treatment of primary dysmenorrhea: a meta-analysis.Altern Ther Health Med. 2014 Jul-Aug;20(4):33-42. Altern Ther Health Med. 2014. PMID: 25141361 Review.
-
Moxibustion for Essential Hypertension and Hypertensive Symptoms: A Systematic Review of 18 Randomized Controlled Trials.Complement Med Res. 2021;28(5):435-445. doi: 10.1159/000513701. Epub 2021 Jan 25. Complement Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33494086 English.
Cited by
-
Acupoint application therapies for essential hypertension: a systematic review and Meta-analysis.J Tradit Chin Med. 2022 Apr;42(2):159-166. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2022.02.001. J Tradit Chin Med. 2022. PMID: 35473335 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of moxibustion for patients with functional constipation: A protocol for systematic review and meta analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jul 10;99(28):e20910. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020910. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32664085 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Artemisia Vulgaris L. (Common Mugwort) in the History of Medicine and Its Possible Contemporary Applications Substantiated by Phytochemical and Pharmacological Studies.Molecules. 2020 Sep 25;25(19):4415. doi: 10.3390/molecules25194415. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32992959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Moxibustion Promotes Formation of Granulation in Wound Healing Process through Induction of Transforming Growth Factor-β in Rats.Chin J Integr Med. 2020 Jan;26(1):26-32. doi: 10.1007/s11655-019-3083-x. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Chin J Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 31776965
-
Low-level laser treatment applied at auriculotherapy points to reduce postoperative pain in third molar surgery: A randomized, controlled, single-blinded study.PLoS One. 2018 Jun 19;13(6):e0197989. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0197989. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29920521 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. The Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’Collaboration. Effects of different blood pressure lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: second cycle of prospectively designed overviews. The Lancet. 2003;362:1527–1535. - PubMed
-
- Shaw E, Anderson JG, Maloney M, Jay SJ, Fagan D. Factors associated with noncompliance of patients taking antihypertensive medications. Hospital Pharmacy. 1995;30(3):201–203. - PubMed
-
- Bailey JE, Lee MD, Somes GW, Graham RL. Risk factors for antihypertensive medication refill failure by patients under medicaid managed care. Clinical Therapeutics. 1996;18(6):1252–1262. - PubMed
-
- Wood MJ, Stewart RL, Merry H, Johnstone DE, Cox JL. Use of complementary and alternative medical therapies in patients with cardiovascular disease. American Heart Journal. 2003;145(5):806–812. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

