Effectiveness of Stimulation of Acupoint KI 1 by Artemisia vulgaris (Moxa) for the Treatment of Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 24744807
- PMCID: PMC3972940
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/187484
Effectiveness of Stimulation of Acupoint KI 1 by Artemisia vulgaris (Moxa) for the Treatment of Essential Hypertension: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Objective. A systematic review of randomized controlled trials has been performed to assess the effectiveness of stimulation of acupoint KI 1 by Artemisia vulgaris (the Japanese name is moxa) to lower blood pressure compared to antihypertensive drugs. Methods and Findings. Articles published from 1980 to August 2013 in databases of CENTRAL, Pubmed, CBM, CNKI, VIP, and online clinical trial registry websites were searched. Studies included were randomized controlled trials (RCTs); moxibustion-type intervention on KI 1 compared with antihypertensive drugs; meta-analysis showed superior effects of moxibustion plus antihypertensive drugs on systolic blood pressure (WMD: -4.91 [-7.54, -2.28]; P = 0.0003) but no superior effects on diastolic blood pressure (WMD: -6.38 [-17.17, 4.41]; P = 0.25). Conclusions. Our systematic review of the current literature shows a beneficial effect of using moxibustion interventions on KI 1 to lower blood pressure compared to antihypertensive drugs. However, the results are influenced by the existing differences in design of the current trials.
Figures

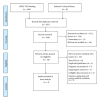

References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. The Lancet. 2005;365(9455):217–223. - PubMed
-
- Blood Pressure Lowering Treatment Trialists’Collaboration. Effects of different blood pressure lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: second cycle of prospectively designed overviews. The Lancet. 2003;362:1527–1535. - PubMed
-
- Shaw E, Anderson JG, Maloney M, Jay SJ, Fagan D. Factors associated with noncompliance of patients taking antihypertensive medications. Hospital Pharmacy. 1995;30(3):201–203. - PubMed
-
- Bailey JE, Lee MD, Somes GW, Graham RL. Risk factors for antihypertensive medication refill failure by patients under medicaid managed care. Clinical Therapeutics. 1996;18(6):1252–1262. - PubMed
-
- Wood MJ, Stewart RL, Merry H, Johnstone DE, Cox JL. Use of complementary and alternative medical therapies in patients with cardiovascular disease. American Heart Journal. 2003;145(5):806–812. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

