Pott's Disease in a 2-Year-Old Child Treated by Decompression and Anterior-Posterior Instrumented Fusion
- PMID: 24744934
- PMCID: PMC3972882
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/252973
Pott's Disease in a 2-Year-Old Child Treated by Decompression and Anterior-Posterior Instrumented Fusion
Abstract
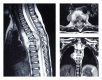
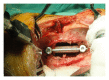
Introduction. Paraplegia and kyphotic deformity are two major disease-related problems of spinal tuberculosis, especially in the early age disease. In this study a 2-year-old boy who underwent surgical decompression, correction, and 360° instrumented fusion via simultaneous anterior-posterior technique for Pott's disease was reported. Case Report. A 2-year-and-9-month-old boy presented with severe back pain and paraparesis of one-month duration. Thoracic magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated destruction with a large paraspinal abscess involving T5-T6-T7 levels, compressing the spinal cord. The paraspinal abscess drained and three-level corpectomy was performed at T5-6-7 with transthoracic approach. Anterior instrumentation and fusion was performed with structural 1 autogenous fibula and rib graft using screw-rod system. In prone position pedicle screws were inserted at T4 and T8 levels and rods were placed. Six months after surgery, there was no weakness or paraparesis and no correction loss at the end of follow-up period. Discussion. In cases of vertebral osteomyelitis with severe anterior column destruction in the very early child ages the use of anterior structural grafts and instrumentation in combination with posterior instrumentation is safe and effective in maintenance of the correction achieved and allows efficient stabilization and early mobilization.
Figures
References
-
- Moon M-S. Spine update tuberculosis of the spine: controversies and a new challenge. Spine. 1997;22(15):1791–1797. - PubMed
-
- Lee T-C, Lu K, Yang L-C, Huang H-Y, Liang C-L. Transpedicular instrumentation as an adjunct in the treatment of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine tuberculosis with early stage bone destruction. Journal of Neurosurgery. 1999;91(2):163–169. - PubMed
-
- Yilmaz C, Selek HY, Gürkan I, Erdemli B, Korkusuz Z. Anterior instrumentation for the treatment of spinal tuberculosis. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery. American. 1999;81(9):1261–1267. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources