Development of Localized Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema in a Late Preterm Infant without Mechanical Ventilation
- PMID: 24744939
- PMCID: PMC3972850
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/429797
Development of Localized Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema in a Late Preterm Infant without Mechanical Ventilation
Abstract
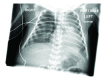
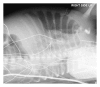
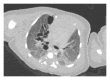
Pulmonary interstitial emphysema (PIE) is not an uncommon finding in premature infants with respiratory distress who need respiratory support by mechanical ventilation. PIE has been reported in a few cases of neonates in whom either no treatment other than room air was given or they were given continuous positive end-expiratory pressure (CPAP) support. We present a case of a premature neonate who presented with respiratory distress, in whom PIE and spontaneous pneumothorax (PTX) developed while on CPAP therapy only. The patient was treated conservatively with subsequent resolution of the radiological findings and clinical improvement. No surgical intervention was required. It is important to know that PIE may develop independently of mechanical ventilation. We would like to add this case to the literature and describe the pertinent plain film and computed tomography (CT) findings of this entity, the possible mechanism of development, and the differential diagnosis. A review of the literature is also provided.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Positional treatment without mechanical ventilation in a very preterm infant with unilateral pulmonary interstitial emphysema: case report and review of the literature.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Aug 1;19(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1640-2. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31370828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unilateral neonatal pulmonary interstitial emphysema managed conservatively: A case report.Pediatr Pulmonol. 2021 Jan;56(1):83-87. doi: 10.1002/ppul.25112. Epub 2020 Oct 20. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2021. PMID: 33080119
-
Pulmonary interstitial emphysema after resolution of relapsing pneumothorax and discontinuation of mechanical ventilation. An atypical case in a preterm infant.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014 Oct;27(15):1610-2. doi: 10.3109/14767058.2013.867322. Epub 2013 Dec 16. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014. PMID: 24245490
-
Localized persistent pulmonary interstitial emphysema in a preterm infant in the absence of mechanical ventilation.Pediatr Radiol. 2005 Dec;35(12):1243-5. doi: 10.1007/s00247-005-1562-z. Epub 2005 Aug 16. Pediatr Radiol. 2005. PMID: 16086158
-
CT imaging of pulmonary lobar interstitial emphysema in a spontaneous breathing preterm infant.Am J Perinatol. 2002 Aug;19(6):285-90. doi: 10.1055/s-2002-34466. Am J Perinatol. 2002. PMID: 12357418 Review.
Cited by
-
Diffuse persistent pulmonary interstitial emphysema secondary to mechanical ventilation in bronchiolitis.BMC Pulm Med. 2016 Nov 3;16(1):139. doi: 10.1186/s12890-016-0299-9. BMC Pulm Med. 2016. PMID: 27809884 Free PMC article.
-
Positional treatment without mechanical ventilation in a very preterm infant with unilateral pulmonary interstitial emphysema: case report and review of the literature.BMC Pediatr. 2019 Aug 1;19(1):267. doi: 10.1186/s12887-019-1640-2. BMC Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31370828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Persistent Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema With Respiratory Infection: A Clinicopathological Analysis of Six Cases and Detection of Infectious Pathogens by Metagenomic Next-Generation Sequencing (mNGS).Front Pediatr. 2022 Apr 7;10:836276. doi: 10.3389/fped.2022.836276. eCollection 2022. Front Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 35463878 Free PMC article.
-
A Case of Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema Treated by Percutaneous Catheter Insertion in Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant.Yonsei Med J. 2016 Nov;57(6):1523-6. doi: 10.3349/ymj.2016.57.6.1523. Yonsei Med J. 2016. PMID: 27593885 Free PMC article.
-
Early Pulmonary Interstitial Emphysema in Preterm Neonates-Respiratory Management and Case Report in Nonventilated Very Low Birth Weight Twins.AJP Rep. 2018 Apr;8(2):e99-e105. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1648253. Epub 2018 May 14. AJP Rep. 2018. PMID: 29765788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Crosswell HE, Stewart DL. Special feature: radiological case of the month. Pulmonary interstitial emphysema in a nonventilated preterm infant. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine. 2001;155(5):615–616. - PubMed
-
- Al-Abdi SY, Singhal N. Pulmonary interstitial emphysema and continuous positive airway pressure in a premature infant. Saudi Medical Journal. 2005;26(10):1627–1629. - PubMed
-
- Berk DR, Varich LJ. Localized persistent pulmonary interstitial emphysema in a preterm infant in the absence of mechanical ventilation. Pediatric Radiology. 2005;35(12):1243–1245. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

