The utility of a novel triple marker (combination of TTF1, napsin A, and p40) in the subclassification of non-small cell lung cancer
- PMID: 24746197
- PMCID: PMC4178947
- DOI: 10.1016/j.humpath.2014.01.005
The utility of a novel triple marker (combination of TTF1, napsin A, and p40) in the subclassification of non-small cell lung cancer
Abstract
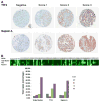
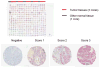
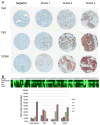
In lung cancer, targeted therapies depend on accurate histological subclassification of the tumor. The majority of lung cancers can be subclassified based on hematoxylin and eosin staining; however, classification may be difficult in small biopsies. In this study, we investigated the utility of a newly developed triple marker (combination of TTF1/Napsin A/p40) and compared the sensitivity and specificity of this novel marker with individual markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinomas. Lung cancer tissue microarrays were constructed using surgical resection material from the Johns Hopkins Hospital. They included 77 adenocarcinomas (ADCs), 77 squamous cell carcinomas (SqCCs), and 46 cases of metastatic lung ADCs. Immunostaining patterns of all markers were scored semi-quantitatively and compared. In ADCs, the sensitivity and specificity of the triple marker were 93.5% and 77.5%, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity of TTF1 and Napsin A were 85.7% and 75.0%, and 89.6% and 90.0%. In SqCCs, the sensitivity and specificity of the triple marker were 88.3% and 92.5%, while the p40, p63 and CK5/6 showed 80.5% and 90.0%; 93.5% and 80.0%; and 89.6% and 80.0%. In addition, the sensitivity and specificity of the triple marker in metastatic ADCs showed 71.7% and 73.5%, respectively. Our triple marker (combination of TTF1/Napsin A/p40) showed a similar sensitivity and specificity for the subclassification of NSCLC when compared to individual markers. Our study not only demonstrates a useful combination of immunomarkers but also optimally conserves tissue for molecular marker testing.
Keywords: Immunohistochemical markers; Napsin A; Non–small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC); Novel triple stain marker; P40.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Utility of a novel triple marker (combination of thyroid transcription factor 1, Napsin A, and P40) in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinomas using fine-needle aspiration cases.Hum Pathol. 2016 Aug;54:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2016.02.027. Epub 2016 Apr 1. Hum Pathol. 2016. PMID: 27045515
-
Subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinomas lacking morphologic differentiation on biopsy specimens: Utility of an immunohistochemical panel containing TTF-1, napsin A, p63, and CK5/6.Am J Surg Pathol. 2011 Jan;35(1):15-25. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182036d05. Am J Surg Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21164283
-
Napsin A/p40 antibody cocktail for subtyping non-small cell lung carcinoma on cytology and small biopsy specimens.Cancer Cytopathol. 2016 Jul;124(7):472-84. doi: 10.1002/cncy.21707. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Cancer Cytopathol. 2016. PMID: 27412420
-
When tumor doesn't read textbook. Third case of TTF1 and p40 co-expression in the same tumour cells in a non-small cell carcinoma. A potential new entity to consider?Pathologica. 2019 Jun;111(2):58-61. doi: 10.32074/1591-951X-12-19. Pathologica. 2019. PMID: 31388196 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TP53, NOTCH2, and STK11 Mutations in a Rare Tumor of non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma with Diffuse Coexpression of TTF1 and p40 in the Same Tumor Cells.Int J Surg Pathol. 2023 Sep;31(6):1041-1047. doi: 10.1177/10668969221126105. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Int J Surg Pathol. 2023. PMID: 36253711 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-World Diagnostic Accuracy and Use of Immunohistochemical Markers in Lung Cancer Diagnostics.Biomolecules. 2021 Nov 18;11(11):1721. doi: 10.3390/biom11111721. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34827719 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of p16 and p53 in non-small-cell lung cancer: clinicopathological correlation and potential prognostic impact.Biomark Med. 2019 Jun;13(9):761-771. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2018-0441. Epub 2019 Jun 3. Biomark Med. 2019. PMID: 31157548 Free PMC article.
-
Utility of five commonly used immunohistochemical markers TTF-1, Napsin A, CK7, CK5/6 and P63 in primary and metastatic adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma of the lung: a retrospective study of 246 fine needle aspiration cases.Clin Transl Med. 2015 Apr 21;4:16. doi: 10.1186/s40169-015-0057-2. eCollection 2015. Clin Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25977750 Free PMC article.
-
The expression of TTF-1 and Napsin A in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma correlates with the results of surgical treatment.Tumour Biol. 2015 Sep;36(10):8085-92. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-3478-z. Epub 2015 May 16. Tumour Biol. 2015. PMID: 25982999
-
[Significance of immunohistochemical indicators in diagnosis and prognosis of squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma of lung].Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014 Jun 20;17(6):506-10. doi: 10.3779/j.issn.1009-3419.2014.06.13. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2014. PMID: 24949694 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese. No abstract available.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2012;62:10–29. - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Spreafico A, Novello S, Wood MD, Simms L, Papotti M. The prognostic and predictive role of histology in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a literature review. J Thorac Oncol. 2008;3:1468–81. - PubMed
-
- Janku F, Garrido-Laguna I, Petruzelka LB, Stewart DJ, Kurzrock R. Novel therapeutic targets in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:1601–12. Review. - PubMed
-
- Munfus-McCray D, Cui M, Zhang Z, Askin F, Gabrielson E, Li QK. Comparison of EGFR and KRAS mutations in primary and unpaired metastatic lung adenocarcinoma with potential chemotherapy effect. HUM PATHOL. 2011;42:1447–53. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

