Resident progenitors, not exogenous migratory cells, generate the majority of visceral mesothelium in organogenesis
- PMID: 24746591
- PMCID: PMC4037704
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.04.003
Resident progenitors, not exogenous migratory cells, generate the majority of visceral mesothelium in organogenesis
Abstract
Historically, analyses of mesothelial differentiation have focused on the heart where a highly migratory population of progenitors originating from a localized "extrinsic" source moves to and over the developing organ. This model long stood alone as the paradigm for generation of this cell type. Here, using chick/quail chimeric grafting and subsequent identification of mesothelial cell populations, we demonstrate that a different mechanism for the generation of mesothelia exists in vertebrate organogenesis. In this newly discovered model, mesothelial progenitors are intrinsic to organs of the developing digestive and respiratory systems. Additionally, we demonstrate that the early heart stands alone in its ability to recruit an entirely exogenous mesothelial cell layer during development. Thus, the newly identified "organ intrinsic" model of mesotheliogenesis appears to predominate while the long-studied cardiac model of mesothelial development may be the outlier.
Keywords: Mesothelia; Organogenesis; coelomate.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

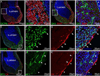



References
-
- Wilm B, Ipenberg A, Hastie ND, Burch JB, Bader DM. The serosal mesothelium is a major source of smooth muscle cells of the gut vasculature. Development. 2005;132(23):5317–5328. - PubMed
-
- Dettman RW, Denetclaw W, Jr, Ordahl CP, Bristow J. Common epicardial origin of coronary vascular smooth muscle, perivascular fibroblasts, and intermyocardial fibroblasts in the avian heart. Dev Biol. 1998;193(2):169–181. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

