Pancreatic β cell dedifferentiation in diabetes and redifferentiation following insulin therapy
- PMID: 24746806
- PMCID: PMC4067979
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.03.010
Pancreatic β cell dedifferentiation in diabetes and redifferentiation following insulin therapy
Abstract
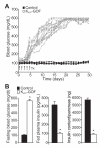
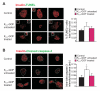
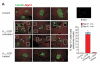
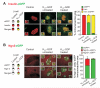
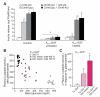
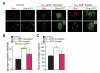
Diabetes is characterized by "glucotoxic" loss of pancreatic β cell function and insulin content, but underlying mechanisms remain unclear. A mouse model of insulin-secretory deficiency induced by β cell inexcitability (K(ATP) gain of function) demonstrates development of diabetes and reiterates the features of human neonatal diabetes. In the diabetic state, β cells lose their mature identity and dedifferentiate to neurogenin3-positive and insulin-negative cells. Lineage-tracing experiments show that dedifferentiated cells can subsequently redifferentiate to mature neurogenin3-negative, insulin-positive β cells after lowering of blood glucose by insulin therapy. We demonstrate here that β cell dedifferentiation, rather than apoptosis, is the main mechanism of loss of insulin-positive cells, and redifferentiation accounts for restoration of insulin content and antidiabetic drug responsivity in these animals. These results may help explain gradual decrease in β cell mass in long-standing diabetes and recovery of β cell function and drug responsivity in type 2 diabetic patients following insulin therapy, and they suggest an approach to rescuing "exhausted" β cells in diabetes.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Ahlqvist E, Ahluwalia TS, Groop L. Genetics of type 2 diabetes. Clin Chem. 2011;57:241–254. - PubMed
-
- Ahren B. Type 2 diabetes, insulin secretion and beta-cell mass. Curr Mol Med. 2005;5:275–286. - PubMed
-
- Alvarsson M, Sundkvist G, Lager I, Berntorp K, Fernqvist-Forbes E, Steen L, Orn T, Holberg MA, Kirksaether N, Grill V. Effects of insulin vs. glibenclamide in recently diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes: a 4-year follow-up. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2008;10:421–429. - PubMed
-
- Alvarsson M, Sundkvist G, Lager I, Henricsson M, Berntorp K, Fernqvist-Forbes E, Steen L, Westermark G, Westermark P, Orn T, et al. Beneficial effects of insulin versus sulphonylurea on insulin secretion and metabolic control in recently diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care. 2003;26:2231–2237. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

