Cellular foundations of mammary tubulogenesis
- PMID: 24747369
- PMCID: PMC4116098
- DOI: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.04.019
Cellular foundations of mammary tubulogenesis
Abstract
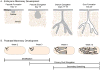
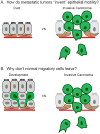
The mammary gland is composed of a highly branched network of epithelial tubes, embedded within a complex stroma. The mammary epithelium originates during embryonic development from an epidermal placode. However, the majority of ductal elongation and bifurcation occurs postnatally, in response to steroid hormone and growth factor receptor signaling. The process of pubertal branching morphogenesis involves both elongation of the primary ducts across the length of the fat pad and a wave of secondary branching that elaborates the ductal network. Recent studies have revealed that mammary epithelial morphogenesis is accomplished by transitions between simple and stratified organization. During active morphogenesis, the epithelium is stratified, highly proliferative, has few intercellular junctions, and exhibits incomplete apico-basal polarity. In this review, we discuss recent advances in our understanding of the relationship between epithelial architecture, epithelial polarity, and ductal elongation.
Keywords: Apico-basal polarity; Branching morphogenesis; Breast cancer; Collective cell migration; Mammary gland; Tubulogenesis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
-
- O’Brien LE, Zegers MM, Mostov KE. Opinion: Building epithelial architecture: insights from three-dimensional culture models. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2002;3:531–537. - PubMed
-
- Bilder D. Epithelial polarity and proliferation control: links from the Drosophila neoplastic tumor suppressors. Genes Dev. 2004;18:1909–1925. - PubMed
-
- McNally S, Martin F. Molecular regulators of pubertal mammary gland development. Ann Med. 2011;43:212–234. - PubMed
-
- Veltmaat JM, Mailleux AA, Thiery JP, Bellusci S. Mouse embryonic mammogenesis as a model for the molecular regulation of pattern formation. Differentiation. 2003;71:1–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

