An integrin β₃-KRAS-RalB complex drives tumour stemness and resistance to EGFR inhibition
- PMID: 24747441
- PMCID: PMC4105198
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb2953
An integrin β₃-KRAS-RalB complex drives tumour stemness and resistance to EGFR inhibition
Abstract
Tumour cells, with stem-like properties, are highly aggressive and often show drug resistance. Here, we reveal that integrin α(v)β₃ serves as a marker of breast, lung and pancreatic carcinomas with stem-like properties that are highly resistant to receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as erlotinib. This was observed in vitro and in mice bearing patient-derived tumour xenografts or in clinical specimens from lung cancer patients who had progressed on erlotinib. Mechanistically, α(v)β₃, in the unliganded state, recruits KRAS and RalB to the tumour cell plasma membrane, leading to the activation of TBK1 and NF-κB. In fact, α(v)β₃ expression and the resulting KRAS-RalB-NF-κB pathway were both necessary and sufficient for tumour initiation, anchorage independence, self-renewal and erlotinib resistance. Pharmacological targeting of this pathway with bortezomib reversed both tumour stemness and erlotinib resistance. These findings not only identify α(v)β₃ as a marker/driver of carcinoma stemness but also reveal a therapeutic strategy to sensitize such tumours to RTK inhibition.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00409968.
Figures

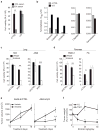

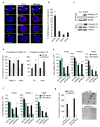

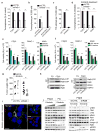
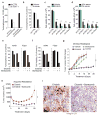

Comment in
-
Targeting the Achilles' heel of drug-resistant cancer stem cells.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(13):2017-8. doi: 10.4161/cc.29460. Epub 2014 Jun 6. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 24906000 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Integrin β3 links therapy resistance and cancer stem cell properties.Nat Cell Biol. 2014 May;16(5):397-9. doi: 10.1038/ncb2960. Nat Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24914436
-
Integrin-mediated resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor-targeted therapy: an inflammatory situation.Breast Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 23;16(5):448. doi: 10.1186/s13058-014-0448-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25255930 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01 CA155620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 CA121938/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA016672/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R3750286/PHS HHS/United States
- R37 CA050286/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA168692/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA168692/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL112962/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32CA121938/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057900/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA45726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL57900/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- CA155620/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA045726/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

