Impact of the loss of caveolin-1 on lung mass and cholesterol metabolism in mice with and without the lysosomal cholesterol transporter, Niemann-Pick type C1
- PMID: 24747682
- PMCID: PMC4035115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.04.002
Impact of the loss of caveolin-1 on lung mass and cholesterol metabolism in mice with and without the lysosomal cholesterol transporter, Niemann-Pick type C1
Abstract
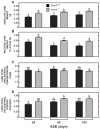
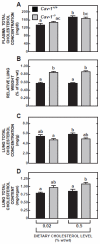
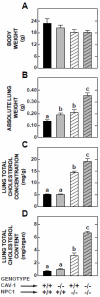
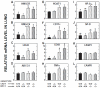
Caveolin-1 (Cav-1) is a major structural protein in caveolae in the plasma membranes of many cell types, particularly endothelial cells and adipocytes. Loss of Cav-1 function has been implicated in multiple diseases affecting the cardiopulmonary and central nervous systems, as well as in specific aspects of sterol and lipid metabolism in the liver and intestine. Lungs contain an exceptionally high level of Cav-1. Parameters of cholesterol metabolism in the lung were measured, initially in Cav-1-deficient mice (Cav-1(-/-)), and subsequently in Cav-1(-/-) mice that also lacked the lysosomal cholesterol transporter Niemann-Pick C1 (Npc1) (Cav-1(-/-):Npc1(-/-)). In 50-day-old Cav-1(-/-) mice fed a low- or high-cholesterol chow diet, the total cholesterol concentration (mg/g) in the lungs was marginally lower than in the Cav-1(+/+) controls, but due to an expansion in their lung mass exceeding 30%, whole-lung cholesterol content (mg/organ) was moderately elevated. Lung mass (g) in the Cav-1(-/-):Npc1(-/-) mice (0.356±0.022) markedly exceeded that in their Cav-1(+/+):Npc1(+/+) controls (0.137±0.009), as well as in their Cav-1(-/-):Npc1(+/+) (0.191±0.013) and Cav-1(+/+):Npc1(-/-) (0.213±0.022) littermates. The corresponding lung total cholesterol contents (mg/organ) in mice of these genotypes were 6.74±0.17, 0.71±0.05, 0.96±0.05 and 3.12±0.43, respectively, with the extra cholesterol in the Cav-1(-/-):Npc1(-/-) and Cav-1(+/+):Npc1(-/-) mice being nearly all unesterified (UC). The exacerbation of the Npc1 lung phenotype and increase in the UC level in the Cav-1(-/-):Npc1(-/-) mice imply a regulatory role of Cav-1 in pulmonary cholesterol metabolism when lysosomal sterol transport is disrupted.
Keywords: Cellular cholesterol trafficking; Cholesterol feeding; Cholesterol synthesis; Pulmonary dysfunction; Relative organ weight.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Repa JJ, Lund EG, Horton JD, Leitersdorf E, Russell DW, Dietschy JM, Turley SD. Disruption of the sterol 27-hydroxylase gene in mice results in hepatomegaly and hypertriglyceridemia. Reversal by cholic acid feeding. J. Biol. Chem. 2000;275:39685–39692. - PubMed
-
- Bates SR, Tao JQ, Collins HL, Francone OL, Rothblat GH. Pulmonary abnormalities due to ABCA1 deficiency in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2005;289:L980–989. - PubMed
-
- Baldan A, Tarr P, Vales CS, Frank J, Shimotake TK, Hawgood S, Edwards PA. Deletion of the transmembrane transporter ABCG1 results in progressive pulmonary lipidosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:29401–29410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

