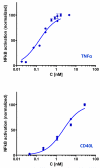
Effects of representative glucocorticoids on TNFα- and CD40L-induced NF-κB activation in sensor cells
- PMID: 24747770
- PMCID: PMC4049353
- DOI: 10.1016/j.steroids.2014.04.003
Effects of representative glucocorticoids on TNFα- and CD40L-induced NF-κB activation in sensor cells
Abstract
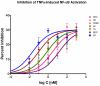
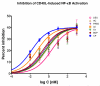
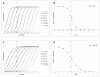
Glucocorticoids are an important class of anti-inflammatory/immunosuppressive drugs. A crucial part of their anti-inflammatory action results from their ability to repress proinflammatory transcription factors such as nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) upon binding to the glucocorticoid receptor (GR). Accordingly, sensor cells quantifying their effect on inflammatory signal-induced NF-κB activation can provide useful information regarding their potencies as well as their transrepression abilities. Here, we report results obtained on their effect in suppressing both the TNFα- and the CD40L-induced activation of NF-κB in sensor cells that contain an NF-κB-inducible SEAP construct. In these cells, we confirmed concentration-dependent NF-κB activation for both TNFα and CD40L at low nanomolar concentrations (EC50). Glucocorticoids tested included hydrocortisone, prednisolone, dexamethasone, loteprednol etabonate, triamcinolone acetonide, beclomethasone dipropionate, and clobetasol propionate. They all caused significant, but only partial inhibition of these activations in concentration-dependent manners that could be well described by sigmoid response-functions. Despite the limitations of only partial maximum inhibitions, this cell-based assay could be used to quantitate the suppressing ability of glucocorticoids (transrepression potency) on the expression of proinflammatory transcription factors caused by two different cytokines in parallel both in a detailed, full dose-response format as well as in a simpler single-dose format. Whereas inhibitory potencies obtained in the TNF assay correlated well with consensus glucocorticoid potencies (receptor-binding affinities, Kd, RBA, at the GR) for all compounds, the non-halogenated steroids (hydrocortisone, prednisolone, and loteprednol etabonate) were about an order of magnitude more potent than expected in the CD40 assay in this system.
Keywords: CD154; Corticosteroids; Hill equation; TNF; Transrepression.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Schimmer BP, Parker KL. Adrenocorticotropic hormone; adrenocortical steroids and their synthetic analogs; inhibitors of the synthesis and actions of adrenocortical hormones. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE, editors. Goodman & Gilman’s The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. McGraw-Hill; New York: 1996. pp. 1459–85.
-
- Barnes PJ. Therapeutic strategies for allergic diseases. Nature. 1999;402(Suppl.):B31–B8. - PubMed
-
- Avery MA, Woolfrey JR. Anti-inflammatory steroids. In: Abraham DJ, editor. Burger’s Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery Vol 3, Cardiovascular Agents and Endocrines. 6th Edition Wiley; Hoboken, NJ: 2003. pp. 747–853.
-
- Bodor N, Buchwald P. Corticosteroid design for the treatment of asthma: structural insights and the therapeutic potential of soft corticosteroids. Curr Pharm Des. 2006;12:3241–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

