Triggering respirofermentative metabolism in the crabtree-negative yeast Pichia guilliermondii by disrupting the CAT8 gene
- PMID: 24747899
- PMCID: PMC4054228
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00854-14
Triggering respirofermentative metabolism in the crabtree-negative yeast Pichia guilliermondii by disrupting the CAT8 gene
Abstract
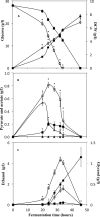
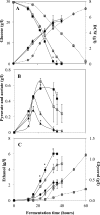
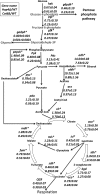
Pichia guilliermondii is a Crabtree-negative yeast that does not normally exhibit respirofermentative metabolism under aerobic conditions, and methods to trigger this metabolism may have applications for physiological study and industrial applications. In the present study, CAT8, which encodes a putative global transcriptional activator, was disrupted in P. guilliermondii. This yeast's ethanol titer increased by >20-fold compared to the wild type (WT) during aerobic fermentation using glucose. A comparative transcriptional analysis indicated that the expression of genes in the tricarboxylic acid cycle and respiratory chain was repressed in the CAT8-disrupted (ΔCAT8) strain, while the fermentative pathway genes were significantly upregulated. The respiratory activities in the ΔCAT8 strain, indicated by the specific oxygen uptake rate and respiratory state value, decreased to one-half and one-third of the WT values, respectively. In addition, the expression of HAP4, a transcriptional respiratory activator, was significantly repressed in the ΔCAT8 strain. Through disruption of HAP4, the ethanol production of P. guilliermondii was also increased, but the yield and titer were lower than that in the ΔCAT8 strain. A further transcriptional comparison between ΔCAT8 and ΔHAP4 strains suggested a more comprehensive reprogramming function of Cat8 in the central metabolic pathways. These results indicated the important role of CAT8 in regulating the glucose metabolism of P. guilliermondii and that the regulation was partially mediated by repressing HAP4. The strategy proposed here might be applicable to improve the aerobic fermentation capacity of other Crabtree-negative yeasts.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transcriptional activator Cat8 is involved in regulation of xylose alcoholic fermentation in the thermotolerant yeast Ogataea (Hansenula) polymorpha.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Feb 28;16(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0652-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 28245828 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Cat8 in energy metabolic balance and glucose tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023 Jul;107(14):4605-4619. doi: 10.1007/s00253-023-12593-2. Epub 2023 May 30. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37249587
-
A single Gal4-like transcription factor activates the Crabtree effect in Komagataella phaffii.Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 21;9(1):4911. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07430-4. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30464212 Free PMC article.
-
Scheffersomyces stipitis: a comparative systems biology study with the Crabtree positive yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Microb Cell Fact. 2012 Oct 9;11:136. doi: 10.1186/1475-2859-11-136. Microb Cell Fact. 2012. PMID: 23043429 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic reconstruction and flux analysis of industrial Pichia yeasts.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013 Mar;97(5):1865-73. doi: 10.1007/s00253-013-4702-7. Epub 2013 Jan 22. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2013. PMID: 23339015 Review.
Cited by
-
Two homologs of the Cat8 transcription factor are involved in the regulation of ethanol utilization in Komagataella phaffii.Curr Genet. 2021 Aug;67(4):641-661. doi: 10.1007/s00294-021-01165-4. Epub 2021 Mar 16. Curr Genet. 2021. PMID: 33725138 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of advanced producers of first- and second-generation ethanol in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and selected species of non-conventional yeasts (Scheffersomyces stipitis, Ogataea polymorpha).J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020 Jan;47(1):109-132. doi: 10.1007/s10295-019-02242-x. Epub 2019 Oct 21. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31637550 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptional activator Cat8 is involved in regulation of xylose alcoholic fermentation in the thermotolerant yeast Ogataea (Hansenula) polymorpha.Microb Cell Fact. 2017 Feb 28;16(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12934-017-0652-6. Microb Cell Fact. 2017. PMID: 28245828 Free PMC article.
-
Increased ethanol production by deletion of HAP4 in recombinant xylose-assimilating Saccharomyces cerevisiae.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015 Dec;42(12):1623-31. doi: 10.1007/s10295-015-1695-5. Epub 2015 Oct 5. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 26438430
-
The impact of transcription factors Znf1, Sip4, Adr1, Tup1, and Hap4 on xylose alcoholic fermentation in the engineered yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2021 Sep;114(9):1373-1385. doi: 10.1007/s10482-021-01607-6. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2021. PMID: 34170419
References
-
- Papon N, Savini V, Lanoue A, Simkin AJ, Crèche J, Giglioli-Guivanc'h N, Clastre M, Courdavanult V, Sibirny AA. 2013. Candida guilliermondii: biotechnological applications, perspectives for biological control, emerging clinical importance and recent advances in genetics. Curr. Genet. 59:73–90. 10.1007/s00294-013-0391-0 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sibirny AA, Boretsky YR. 2009. Pichia guilliermondii, p 113–134 In Satyanarayana T, Kunze G. (ed), Yeast biotechnology: diversity and applications. Springer, New York, NY
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

