Reconstruction of mreB expression in Staphylococcus aureus via a collection of new integrative plasmids
- PMID: 24747904
- PMCID: PMC4054220
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00759-14
Reconstruction of mreB expression in Staphylococcus aureus via a collection of new integrative plasmids
Abstract
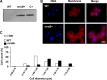
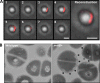
Protein localization has been traditionally explored in unicellular organisms, whose ease of genetic manipulation facilitates molecular characterization. The two rod-shaped bacterial models Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis have been prominently used for this purpose and have displaced other bacteria whose challenges for genetic manipulation have complicated any study of cell biology. Among these bacteria is the spherical pathogenic bacterium Staphylococcus aureus. In this report, we present a new molecular toolbox that facilitates gene deletion in staphylococci in a 1-step recombination process and additional vectors that facilitate the insertion of diverse reporter fusions into newly identified neutral loci of the S. aureus chromosome. Insertion of the reporters does not add any antibiotic resistance genes to the chromosomes of the resultant strains, thereby making them amenable for further genetic manipulations. We used this toolbox to reconstitute the expression of mreB in S. aureus, a gene that encodes an actin-like cytoskeletal protein which is absent in coccal cells and is presumably lost during the course of speciation. We observed that in S. aureus, MreB is organized in discrete structures in association with the membrane, leading to an unusual redistribution of the cell wall material. The production of MreB also caused cell enlargement, but it did not revert staphylococcal shape. We present interactions of MreB with key staphylococcal cell wall-related proteins. This work facilitates the use S. aureus as a model system in exploring diverse aspects of cellular microbiology.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

