Conformational changes required for H(+)/Cl(-) exchange mediated by a CLC transporter
- PMID: 24747941
- PMCID: PMC4040230
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2814
Conformational changes required for H(+)/Cl(-) exchange mediated by a CLC transporter
Abstract
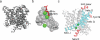
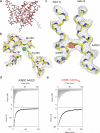
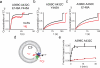
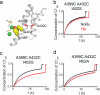
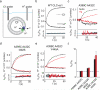
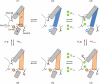
CLC-type exchangers mediate transmembrane Cl(-) transport. Mutations altering their gating properties cause numerous genetic disorders. However, their transport mechanism remains poorly understood. In conventional models, two gates alternatively expose substrates to the intra- or extracellular solutions. A glutamate was identified as the only gate in the CLCs, suggesting that CLCs function by a nonconventional mechanism. Here we show that transport in CLC-ec1, a prokaryotic homolog, is inhibited by cross-links constraining movement of helix O far from the transport pathway. Cross-linked CLC-ec1 adopts a wild-type-like structure, indicating stabilization of a native conformation. Movements of helix O are transduced to the ion pathway via a direct contact between its C terminus and a tyrosine that is a constitutive element of the second gate of CLC transporters. Therefore, the CLC exchangers have two gates that are coupled through conformational rearrangements outside the ion pathway.
Figures

References
-
- Jentsch TJ. CLC chloride channels and transporters: from genes to protein structure, pathology and physiology. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008;43:3–36. - PubMed
-
- Accardi A, Miller C. Secondary active transport mediated by a prokaryotic homologue of ClC Cl− channels. Nature. 2004;427:803–807. - PubMed
-
- Picollo A, Pusch M. Chloride/proton antiporter activity of mammalian CLC proteins ClC-4 and ClC-5. Nature. 2005;436:420–423. - PubMed
-
- Scheel O, Zdebik AA, Lourdel S, Jentsch TJ. Voltage-dependent electrogenic chloride/proton exchange by endosomal CLC proteins. Nature. 2005;436:424–427. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

