Phylogenetic analysis of the endoribonuclease Dicer family
- PMID: 24748168
- PMCID: PMC3991619
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095350
Phylogenetic analysis of the endoribonuclease Dicer family
Abstract
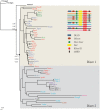
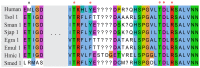
Dicers are proteins of the ribonuclease III family with the ability to process dsRNA, involved in regulation of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Dicers are conserved from basal metazoans to higher metazoans and contain a number of functional domains that interact with dsRNA. The completed genome sequences of over 34 invertebrate species allowed us to systematically investigate Dicer genes over a diverse range of phyla. The majority of invertebrate Dicers clearly fell into the Dicer1 or Dicer2 subfamilies. Most nematodes possessed only one Dicer gene, a member of the Dicer1 subfamily, whereas two Dicer genes (Dicer1 and Dicer2) were present in all platyhelminths surveyed. Analysis of the key domains showed that a 5' pocket was conserved across members of the Dicer1 subfamily, with the exception of the nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Interestingly, Nematostella vectensis DicerB grouped into Dicer2 subfamily harbored a 5' pocket, which is commonly present in Dicer1. Similarly, the 3' pocket was also found to be conserved in all Dicer proteins with the exceptions of Schmidtea mediterranea Dicer2 and Trichoplax adherens Dicer A. The loss of catalytic residues in the RNase III domain was noted in platyhelminths and cnidarians, and the 'ball' and 'socket' junction between two RNase III domains in platyhelminth Dicers was different from the canonical junction, suggesting the possibility of different conformations. The present data suggest that Dicers might have duplicated and diversified independently, and have evolved for various functions in invertebrates.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Multiple dicer genes in the early-diverging metazoa.Mol Biol Evol. 2009 Jun;26(6):1333-40. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msp042. Epub 2009 Mar 10. Mol Biol Evol. 2009. PMID: 19276153
-
Structural and biochemical insights into the dicing mechanism of mouse Dicer: a conserved lysine is critical for dsRNA cleavage.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Feb 19;105(7):2391-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0711506105. Epub 2008 Feb 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 18268334 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of animal and plant dicers: early parallel duplications and recurrent adaptation of antiviral RNA binding in plants.Mol Biol Evol. 2013 Mar;30(3):627-41. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mss263. Epub 2012 Nov 22. Mol Biol Evol. 2013. PMID: 23180579 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Insight into the Domain Structure and Functions of Dicer-Type Ribonucleases.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 9;22(2):616. doi: 10.3390/ijms22020616. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33435485 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism of RNase III action: how dicer dices.Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008;320:99-116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75157-1_5. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18268841 Review.
Cited by
-
Evolution of MicroRNA Biogenesis Genes in the Sterlet (Acipenser ruthenus) and Other Polyploid Vertebrates.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 15;21(24):9562. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249562. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33334059 Free PMC article.
-
The Innate Antiviral Response in Animals: An Evolutionary Perspective from Flagellates to Humans.Viruses. 2019 Aug 16;11(8):758. doi: 10.3390/v11080758. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 31426357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The miRNA biogenesis in marine bivalves.PeerJ. 2016 Mar 7;4:e1763. doi: 10.7717/peerj.1763. eCollection 2016. PeerJ. 2016. PMID: 26989613 Free PMC article.
-
Origin of eukaryotes from within archaea, archaeal eukaryome and bursts of gene gain: eukaryogenesis just made easier?Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015 Sep 26;370(1678):20140333. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2014.0333. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26323764 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biochemical and structural basis of Dicer helicase function unveiled by resurrecting ancient proteins.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Jun 3;122(22):e2500825122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2500825122. Epub 2025 May 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40434637
References
-
- Lamontagne B, Larose S, Boulanger J, Elela SA (2001) The RNase III family: a conserved structure and expanding functions in eukaryotic dsRNA metabolism. Curr Issues Mol Biol 3: 71–78. - PubMed
-
- He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5: 522–531. - PubMed
-
- Hammond SM, Boettcher S, Caudy AA, Kobayashi R, Hannon GJ (2001) Argonaute2, a link between genetic and biochemical analyses of RNAi. Science 293: 1146–1150. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

