Towards an integrative structural biology approach: combining Cryo-TEM, X-ray crystallography, and NMR
- PMID: 24748171
- PMCID: PMC4125826
- DOI: 10.1007/s10969-014-9179-9
Towards an integrative structural biology approach: combining Cryo-TEM, X-ray crystallography, and NMR
Abstract
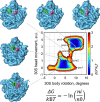
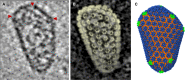
Cryo-transmission electron microscopy (Cryo-TEM) and particularly single particle analysis is rapidly becoming the premier method for determining the three-dimensional structure of protein complexes, and viruses. In the last several years there have been dramatic technological improvements in Cryo-TEM, such as advancements in automation and use of improved detectors, as well as improved image processing techniques. While Cryo-TEM was once thought of as a low resolution structural technique, the method is currently capable of generating nearly atomic resolution structures on a routine basis. Moreover, the combination of Cryo-TEM and other methods such as X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, and molecular dynamics modeling are allowing researchers to address scientific questions previously thought intractable. Future technological developments are widely believed to further enhance the method and it is not inconceivable that Cryo-TEM could become as routine as X-ray crystallography for protein structure determination.
Figures

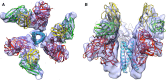

Similar articles
-
Rapid increase of near atomic resolution virus capsid structures determined by cryo-electron microscopy.J Struct Biol. 2018 Jan;201(1):1-4. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Oct 27. J Struct Biol. 2018. PMID: 29080674
-
[Cryo-microscopy, an alternative to the X-ray crystallography?].Med Sci (Paris). 2016 8-9;32(8-9):758-67. doi: 10.1051/medsci/20163208025. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Med Sci (Paris). 2016. PMID: 27615185 Review. French.
-
Cryo electron microscopy to determine the structure of macromolecular complexes.Methods. 2016 Feb 15;95:78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2015.11.023. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Methods. 2016. PMID: 26638773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cryo-electron microscopy and X-ray crystallography: complementary approaches to structural biology and drug discovery.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2017 Apr 1;73(Pt 4):174-183. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X17003740. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2017. PMID: 28368275 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Visualization of biological macromolecules at near-atomic resolution: cryo-electron microscopy comes of age.Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019 Jan 1;75(Pt 1):3-11. doi: 10.1107/S2053230X18015133. Epub 2019 Jan 1. Acta Crystallogr F Struct Biol Commun. 2019. PMID: 30605120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Reporting on the future of integrative structural biology ORAU workshop.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020 Jan 1;25(1):43-68. doi: 10.2741/4794. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2020. PMID: 31585877 Free PMC article.
-
New Era of Studying RNA Secondary Structure and Its Influence on Gene Regulation in Plants.Front Plant Sci. 2018 May 22;9:671. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2018.00671. eCollection 2018. Front Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29872445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
X-ray structure determination using low-resolution electron microscopy maps for molecular replacement.Nat Protoc. 2015 Sep;10(9):1275-84. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.069. Epub 2015 Jul 30. Nat Protoc. 2015. PMID: 26226459 Free PMC article.
-
Delineating distinct heme-scavenging and -binding functions of domains in MF6p/helminth defense molecule (HDM) proteins from parasitic flatworms.J Biol Chem. 2017 May 26;292(21):8667-8682. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.771675. Epub 2017 Mar 27. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28348084 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Methods To Investigate lncRNA and the Influence of lncRNA:Protein Complexes on Chromatin.Biochemistry. 2016 Mar 22;55(11):1615-30. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.5b01141. Epub 2016 Feb 24. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 26859437 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

