The effects of propionate and valerate on insulin responsiveness for glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and C2C12 myotubes via G protein-coupled receptor 41
- PMID: 24748202
- PMCID: PMC3991595
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095268
The effects of propionate and valerate on insulin responsiveness for glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and C2C12 myotubes via G protein-coupled receptor 41
Abstract
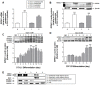
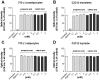
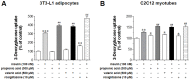
Since insulin resistance can lead to hyperglycemia, improving glucose uptake into target tissues is critical for regulating blood glucose levels. Among the free fatty acid receptor (FFAR) family of G protein-coupled receptors, GPR41 is known to be the Gαi/o-coupled receptor for short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) such as propionic acid (C3) and valeric acid (C5). This study aimed to investigate the role of GPR41 in modulating basal and insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in insulin-sensitive cells including adipocytes and skeletal muscle cells. Expression of GPR41 mRNA and protein was increased with maximal expression at differentiation day 8 for 3T3-L1 adipocytes and day 6 for C2C12 myotubes. GPR41 protein was also expressed in adipose tissues and skeletal muscle. After analyzing dose-response relationship, 300 µM propionic acid or 500 µM valeric acid for 30 min incubation was used for the measurement of glucose uptake. Both propionic acid and valeric acid increased insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocyte, which did not occur in cells transfected with siRNA for GPR41 (siGPR41). In C2C12 myotubes, these SCFAs increased basal glucose uptake, but did not potentiate insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, and siGPR41 treatment reduced valerate-stimulated basal glucose uptake. Therefore, these findings indicate that GPR41 plays a role in insulin responsiveness enhanced by both propionic and valeric acids on glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and C2C12 myotubes, and in valerate-induced increase in basal glucose uptake in C2C12 myotubes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dose-Dependent Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Adipokine Secretion and Metabolic Function.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 4;17(3):571. doi: 10.3390/nu17030571. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940429 Free PMC article.
-
Gαi -coupled GPR41 activation increases Ca2+ influx in C2C12 cells and shows a therapeutic effect in diabetic animals.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2023 Jul;31(7):1871-1883. doi: 10.1002/oby.23786. Epub 2023 Jun 13. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2023. PMID: 37309717
-
Effects of PCB126 on Adipose-to-Muscle Communication in an in Vitro Model.Environ Health Perspect. 2020 Oct;128(10):107002. doi: 10.1289/EHP7058. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Environ Health Perspect. 2020. PMID: 33026256 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of 1-acyl-glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase-alpha enhances lipid storage in cellular models of adipose tissue and skeletal muscle.Diabetes. 2001 Feb;50(2):233-40. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.50.2.233. Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11272131
-
Regulation of Energy Homeostasis by GPR41.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 May 26;5:81. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00081. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 24904531 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Significance of the Enteric Microbiome on the Development of Childhood Disease: A Review of Prebiotic and Probiotic Therapies in Disorders of Childhood.Clin Med Insights Pediatr. 2016 Oct 9;10:91-107. doi: 10.4137/CMPed.S38338. eCollection 2016. Clin Med Insights Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 27774001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on L6 Myotube Inflammatory Mediator Production in Response to Lipopolysaccharide- or Palmitic Acid-Stimulation.Nutrients. 2022 Jul 9;14(14):2826. doi: 10.3390/nu14142826. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 35889783 Free PMC article.
-
Short chain fatty acids and methylamines produced by gut microbiota as mediators and markers in the circulatory system.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020 Jan;245(2):166-175. doi: 10.1177/1535370219900898. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2020. PMID: 31948289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose-Dependent Effects of Short-Chain Fatty Acids on 3T3-L1 Adipocyte Adipokine Secretion and Metabolic Function.Nutrients. 2025 Feb 4;17(3):571. doi: 10.3390/nu17030571. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 39940429 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of selected bioactive food compounds on human white adipocyte function.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016 Jan 19;13:4. doi: 10.1186/s12986-016-0064-3. eCollection 2016. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2016. PMID: 26788115 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parker JC (2002) Troglitazone: the discovery and development of a novel therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 54: 1173–1197. - PubMed
-
- Duncan BB, Schmidt MI, Pankow JS, Ballantyne CM, Couper D, et al. (2003) Low-grade systemic inflammation and the development of type 2 diabetes: the atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes 52: 1799–1805. - PubMed
-
- Lanner JT, Bruton JD, Katz A, Westerblad H (2008) Ca2+ and insulin-mediated glucose uptake. Curr Opin Pharmacol 8: 339–345. - PubMed
-
- Chiasson JL, Rabasa-Lhoret R (2004) Prevention of type 2 diabetes: insulin resistance and β-cell function. Diabetes 53 Suppl 3S34–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

