A phase II trial of Xeloda and oxaliplatin (XELOX) neo-adjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgery for advanced gastric cancer patients with para-aortic lymph node metastasis
- PMID: 24748418
- PMCID: PMC4032640
- DOI: 10.1007/s00280-014-2449-1
A phase II trial of Xeloda and oxaliplatin (XELOX) neo-adjuvant chemotherapy followed by surgery for advanced gastric cancer patients with para-aortic lymph node metastasis
Abstract
Purpose: Gastric cancer with para-aortic lymph node (PAN) involvement is regarded as advanced disease, and only chemotherapy is recommended from the guidelines. In unresectable cases, neoadjuvant chemotherapy could prolong survival if conversion to resectability could be achieved.
Methods: The study was a single-arm phase II trial. Patients who were diagnosed with gastric cancer and PAN involvement (Stations No. 16a2/16b1) were treated with capecitabine and oxaliplatin combination chemotherapy every 3 weeks for a maximum of six cycles. After every two cycles, abdominal computed tomographic scans were repeated to evaluate the response, and surgery was performed at the physician(')s discretion in patients with sufficient tumor response, followed by chemotherapy with the same regimen to complete a total of six cycles. The primary end point was the response rate of the preoperative chemotherapy. The secondary end points were R0 resection rate, progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and adverse events.
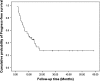
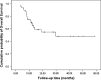
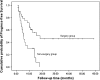
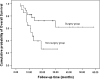
Results: A total of 48 patients were enrolled. The response rate of the first-line chemotherapy was 49.0 %, and the clinical benefit response was 85.1 %. After a median of four cycles of chemotherapy, 28 patients received surgery (58.3 %). The median PFS and OS of all patients were 10.0 and 29.8 months, respectively. Patients in the surgery group had much longer PFS (18.1 vs. 5.6 mo, P = 0.001) and OS (not reached vs. 12.5 mo, P = 0.016) compared with those in the non-surgery group.
Conclusions: For gastric cancer patients with PAN involvement, neoadjuvant chemotherapy with XELOX demonstrated a good response rate, and a sufficient R0 resection rate, with acceptable toxicities. Further study is needed to confirm the effectiveness of this regimen.
Figures
Comment in
-
Gastric cancer with para-aortic lymph node metastases: do not miss a chance of cure!Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;74(2):433-4. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2491-z. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24889718
-
Gastric cancer with para-aortic lymph nodes metastasis: curable dissection possible but be cautiously selected.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014 Aug;74(2):435-6. doi: 10.1007/s00280-014-2512-y. Epub 2014 Jul 15. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25023488
References
-
- Baba M, Hokita S, Natsugoe S, et al. Paraaortic lymphadenectomy in patients with advanced carcinoma of the upper third of the stomach. Hepatogastroenterology. 2000;47(33):893–896. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical