Mitochondria in lung biology and pathology: more than just a powerhouse
- PMID: 24748601
- PMCID: PMC4042189
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00073.2014
Mitochondria in lung biology and pathology: more than just a powerhouse
Abstract
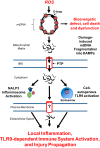
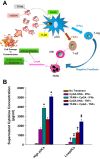
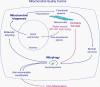
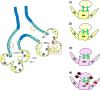
An explosion of new information about mitochondria reveals that their importance extends well beyond their time-honored function as the "powerhouse of the cell." In this Perspectives article, we summarize new evidence showing that mitochondria are at the center of a reactive oxygen species (ROS)-dependent pathway governing the response to hypoxia and to mitochondrial quality control. The potential role of the mitochondrial genome as a sentinel molecule governing cytotoxic responses of lung cells to ROS stress also is highlighted. Additional attention is devoted to the fate of damaged mitochondrial DNA relative to its involvement as a damage-associated molecular pattern driving adverse lung and systemic cell responses in severe illness or trauma. Finally, emerging strategies for replenishing normal populations of mitochondria after damage, either through promotion of mitochondrial biogenesis or via mitochondrial transfer, are discussed.
Keywords: hypoxia; lung injury; mitochondrial biogenesis; mitochondrial transfer; mtDNA.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmad T, Mukherjee S, Pattnaik B, Kumar M, Singh S, Kumar M, Rehman R, Tiwari BK, Jha KA, Barhanpurkar AP, Wani MR, Roy SS, Mabalirajan U, Ghosh B, Agrawal A. Miro1 regulates intercellular mitochondrial transport & enhances mesenchymal stem cell rescue efficacy. EMBO J 2014. February 6 [Epub ahead of print] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Archer SL, Souil E, Dinh-Xuan AT, Schremmer B, Mercier JC, El Yaagoubi A, Nguyen-Huu L, Reeve HL, Hampl V. Molecular identification of the role of voltage-gated K+ channels, Kv1.5 and Kv2.1, in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and control of resting membrane potential in rat pulmonary artery myocytes. J Clin Invest 101: 2319–2330, 1998 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arimori Y, Nakamura R, Yamada H, Shibata K, Maeda N, Kase T, Yoshikai Y. Type I interferon limits influenza virus-induced acute lung injury by regulation of excessive inflammation in mice. Antiviral Res 99: 230–237, 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

