Lung fibroblasts accelerate wound closure in human alveolar epithelial cells through hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling
- PMID: 24748602
- PMCID: PMC4080284
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00233.2013
Lung fibroblasts accelerate wound closure in human alveolar epithelial cells through hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling
Abstract
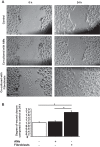
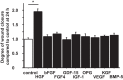
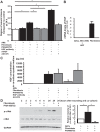
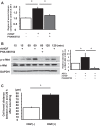
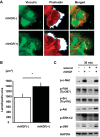
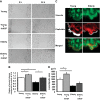
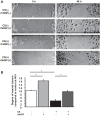
There are 190,600 cases of acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI/ARDS) each year in the United States, and the incidence and mortality of ALI/ARDS increase dramatically with age. Patients with ALI/ARDS have alveolar epithelial injury, which may be worsened by high-pressure mechanical ventilation. Alveolar type II (ATII) cells are the progenitor cells for the alveolar epithelium and are required to reestablish the alveolar epithelium during the recovery process from ALI/ARDS. Lung fibroblasts (FBs) migrate and proliferate early after lung injury and likely are an important source of growth factors for epithelial repair. However, how lung FBs affect epithelial wound healing in the human adult lung has not been investigated in detail. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) is known to be released mainly from FBs and to stimulate both migration and proliferation of primary rat ATII cells. HGF is also increased in lung tissue, bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, and serum in patients with ALI/ARDS. Therefore, we hypothesized that HGF secreted by FBs would enhance wound closure in alveolar epithelial cells (AECs). Wound closure was measured using a scratch wound-healing assay in primary human AEC monolayers and in a coculture system with FBs. We found that wound closure was accelerated by FBs mainly through HGF/c-Met signaling. HGF also restored impaired wound healing in AECs from the elderly subjects and after exposure to cyclic stretch. We conclude that HGF is the critical factor released from FBs to close wounds in human AEC monolayers and suggest that HGF is a potential strategy for hastening alveolar repair in patients with ALI/ARDS.
Keywords: alveolar epithelial cells; hepatocyte growth factor; lung fibroblasts; wound closure.
Copyright © 2014 the American Physiological Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Influenza induces IL-8 and GM-CSF secretion by human alveolar epithelial cells through HGF/c-Met and TGF-α/EGFR signaling.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015 Jun 1;308(11):L1178-88. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00290.2014. Epub 2015 Apr 10. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26033355 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of hepatocyte growth factor secretion by fibroblasts in patients with acute lung injury.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008 Feb;294(2):L334-43. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00096.2007. Epub 2007 Dec 7. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 18065658
-
The cellular kinetics of lung alveolar epithelial cells and its relationship with lung tissue repair after acute lung injury.Respir Res. 2016 Dec 7;17(1):164. doi: 10.1186/s12931-016-0480-y. Respir Res. 2016. PMID: 27923370 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of alveolar epithelial repair in acute lung injury--a translational approach.Swiss Med Wkly. 2003 Nov 22;133(43-44):586-90. doi: 10.4414/smw.2003.10267. Swiss Med Wkly. 2003. PMID: 14745653 Review.
-
[Keratinocyte growth factor and Hepatocyte growth factor: their roles in alveolar epithelial repair].Rev Mal Respir. 2003 Dec;20(6 Pt 1):896-903. Rev Mal Respir. 2003. PMID: 14743091 Review. French.
Cited by
-
The effect of yacon (Samallanthus sonchifolius) ethanol extract on cell proliferation and migration of C6 glioma cells stimulated with fetal bovine serum.Nutr Res Pract. 2015 Jun;9(3):256-61. doi: 10.4162/nrp.2015.9.3.256. Epub 2015 Mar 6. Nutr Res Pract. 2015. PMID: 26060537 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the lung endothelial niche to promote angiogenesis and regeneration: A review of applications.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Dec 19;9:1093369. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.1093369. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 36601582 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activated prostaglandin D2 receptors on macrophages enhance neutrophil recruitment into the lung.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016 Mar;137(3):833-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.11.012. Epub 2016 Jan 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26792210 Free PMC article.
-
Stanniocalcin-1 is induced by hypoxia inducible factor in rat alveolar epithelial cells.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014 Oct 3;452(4):1091-7. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.09.060. Epub 2014 Sep 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014. PMID: 25251473 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomic characterization and localization of phospholipids in the human lung.J Lipid Res. 2017 May;58(5):926-933. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M074955. Epub 2017 Mar 9. J Lipid Res. 2017. PMID: 28280112 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams DH, McIntosh D, Wormald PJ, Cowin AJ. Differential effects of insulin-like growth factors on scratch wound repair in respiratory epithelial cells. Am J Rhinol 20: 652–657, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Arnesen SM, Lawson MA. Age-related changes in focal adhesions lead to altered cell behavior in tendon fibroblasts. Mech Ageing Dev 127: 726–732, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Chesnutt AN, Kheradmand F, Folkesson HG, Alberts M, Matthay MA. Soluble transforming growth factor-alpha is present in the pulmonary edema fluid of patients with acute lung injury. Chest 111: 652–656, 1997 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

