Sulfolobus replication factor C stimulates the activity of DNA polymerase B1
- PMID: 24748616
- PMCID: PMC4054168
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01552-14
Sulfolobus replication factor C stimulates the activity of DNA polymerase B1
Abstract
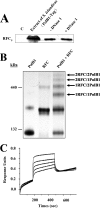
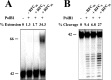
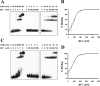
Replication factor C (RFC) is known to function in loading proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) onto primed DNA, allowing PCNA to tether DNA polymerase for highly processive DNA synthesis in eukaryotic and archaeal replication. In this report, we show that an RFC complex from the hyperthermophilic archaea of the genus Sulfolobus physically interacts with DNA polymerase B1 (PolB1) and enhances both the polymerase and 3'-5' exonuclease activities of PolB1 in an ATP-independent manner. Stimulation of the PolB1 activity by RFC is independent of the ability of RFC to bind DNA but is consistent with the ability of RFC to facilitate DNA binding by PolB1 through protein-protein interaction. These results suggest that Sulfolobus RFC may play a role in recruiting DNA polymerase for efficient primer extension, in addition to clamp loading, during DNA replication.
Copyright © 2014, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Assembly and distributive action of an archaeal DNA polymerase holoenzyme.J Mol Biol. 2013 Nov 29;425(23):4820-36. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2013.09.003. Epub 2013 Sep 11. J Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24035812
-
Sulfolobus chromatin proteins modulate strand displacement by DNA polymerase B1.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Sep;41(17):8182-95. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt588. Epub 2013 Jul 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23821667 Free PMC article.
-
On the mechanism of loading the PCNA sliding clamp by RFC.Mol Microbiol. 2008 Apr;68(1):216-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06150.x. Epub 2008 Feb 26. Mol Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 18312273
-
Functions of Multiple Clamp and Clamp-Loader Complexes in Eukaryotic DNA Replication.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;1042:135-162. doi: 10.1007/978-981-10-6955-0_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017. PMID: 29357057 Review.
-
The replication clamp-loading machine at work in the three domains of life.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006 Oct;7(10):751-61. doi: 10.1038/nrm2022. Epub 2006 Sep 6. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16955075 Review.
References
-
- Henneke G, Gueguen Y, Flament D, Azam P, Querellou J, Dietrich J, Hubscher U, Raffin JP. 2002. Replication factor C from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus abyssi does not need ATP hydrolysis for clamp-loading and contains a functionally conserved RFC PCNA-binding domain. J. Mol. Biol. 323:795–810. 10.1016/S0022-2836(02)01028-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

