Long-term memory: A review and meta-analysis of studies of declarative and procedural memory in specific language impairment
- PMID: 24748707
- PMCID: PMC3986888
- DOI: 10.1097/01.tld.0000437939.01237.6a
Long-term memory: A review and meta-analysis of studies of declarative and procedural memory in specific language impairment
Abstract
This review examined the status of long-term memory systems in specific language impairment (SLI), in particular declarative memory and aspects of procedural memory. Studies included in the review were identified following a systematic search of the literature and findings combined using meta-analysis. This review showed individuals with SLI are poorer than age matched controls in the learning and retrieval of verbal information from the declarative memory. However, there is evidence to suggest that the problems with declarative learning and memory for verbal information in SLI might be due to difficulties with verbal working memory and language. The learning and retrieval of non-verbal information from declarative memory appears relatively intact. In relation to procedural learning and memory, evidence indicates poor implicit learning of verbal information. Findings pertaining to nonverbal information have been mixed. This review of the literature indicates there are now substantial grounds for suspecting that multiple memory systems may be implicated in the impairment.
Figures
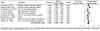
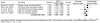



References
-
- Alexander GE, Crutcher MD. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends in Neurosciences. 1990;13:266–271. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, DeLong MR, Strick PL. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annual Review of Neuroscience. 1986;9:357–381. - PubMed
-
- Alloway TP, Gathercole SE. Working memory and neurodevelopmental disorders. Psychology Press; 2012. - PubMed
-
- Archibald L, Gathercole SE. Visuospatial immediate memory in specific language impairment. Journal of Speech, Language and Hearing Research. 2006a;49:265–277. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
