Iron-Loaded Magnetic Nanocapsules for pH-Triggered Drug Release and MRI Imaging
- PMID: 24748722
- PMCID: PMC3988683
- DOI: 10.1021/cm404168a
Iron-Loaded Magnetic Nanocapsules for pH-Triggered Drug Release and MRI Imaging
Abstract
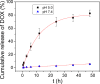
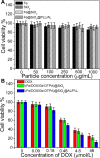
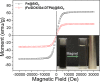
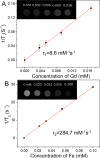
Magnetic nanocapsules were synthesized for controlled drug release, magnetically assisted delivery, and MRI imaging. These magnetic nanocapsules, consisting of a stable iron nanocore and a mesoporous silica shell, were synthesized by controlled encapsulation of ellipsoidal hematite in silica, partial etching of the hematite core in acid, and reduction of the core by hydrogen. The iron core provided a high saturation magnetization and was stable against oxidation for at least 6 months in air and 1 month in aqueous solution. The hollow space between the iron core and mesoporous silica shell was used to load anticancer drug and a T1-weighted MRI contrast agent (Gd-DTPA). These multifunctional monodispersed magnetic "nanoeyes" were coated by multiple polyelectrolyte layers of biocompatible poly-l-lysine and sodium alginate to control the drug release as a function of pH. We studied pH-controlled release, magnetic hysteresis curves, and T1/T2 MRI contrast of the magnetic nanoeyes. They also served as MRI contrast agents with relaxivities of 8.6 mM-1 s-1 (r1) and 285 mM-1 s-1 (r2).
Figures
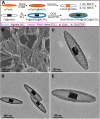
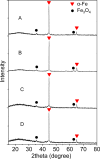
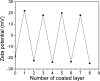
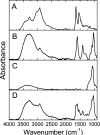
Similar articles
-
Multifunctional yolk-in-shell nanoparticles for pH-triggered drug release and imaging.Small. 2014 Aug 27;10(16):3364-70. doi: 10.1002/smll.201303769. Epub 2014 Apr 19. Small. 2014. PMID: 24753264 Free PMC article.
-
Core/shell structured hollow mesoporous nanocapsules: a potential platform for simultaneous cell imaging and anticancer drug delivery.ACS Nano. 2010 Oct 26;4(10):6001-13. doi: 10.1021/nn1015117. ACS Nano. 2010. PMID: 20815402
-
In vitro and Bioimaging Studies of Mesoporous Silica Nanocomposites Encapsulated Iron-oxide and Loaded Doxorubicin Drug (DOX/IO@Silica) as Magnetically Guided Drug Delivery System.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023;24(10):1297-1306. doi: 10.2174/1389201023666220428084920. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37254276
-
Iron Oxide@Mesoporous Silica Core-Shell Nanoparticles as Multimodal Platforms for Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Magnetic Hyperthermia, Near-Infrared Light Photothermia, and Drug Delivery.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Apr 12;13(8):1342. doi: 10.3390/nano13081342. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37110927 Free PMC article. Review.
-
pH sensitive core-shell magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery in cancer therapy.Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016;57(1):23-32. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2016. PMID: 27151685 Review.
Cited by
-
Pro-organic radical contrast agents ("pro-ORCAs") for real-time MRI of pro-drug activation in biological systems.Polym Chem. 2020 Aug 7;11(29):4768-4779. doi: 10.1039/d0py00558d. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Polym Chem. 2020. PMID: 33790990 Free PMC article.
-
Development of multifunctional nanocomposites for controlled drug delivery and hyperthermia.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 9;11(1):5528. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-84927-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33750868 Free PMC article.
-
Guidable Thermophoretic Janus Micromotors Containing Gold Nanocolorifiers for Infrared Laser Assisted Tissue Welding.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2016 Sep 1;3(12):1600206. doi: 10.1002/advs.201600206. eCollection 2016 Dec. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2016. PMID: 27981009 Free PMC article.
-
From detection to elimination: iron-based nanomaterials driving tumor imaging and advanced therapies.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 7;15:1536779. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1536779. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39990682 Free PMC article. Review.
-
X-ray excited luminescence spectroscopy and imaging with NaGdF4:Eu and Tb.RSC Adv. 2021 Sep 24;11(50):31717-31726. doi: 10.1039/d1ra05451a. eCollection 2021 Sep 21. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35496840 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Morelli D.; Ménard S.; Colnaghi M. I; Balsari A. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 2082–2085. - PubMed
-
- Von Hoff D. D.; Layard M. W.; Basa P.; Davis J. H. L.; Von Hoff A. L.; Rozencweig M.; Muggia F. M. Ann. Intern. Med. 1979, 91, 710–717. - PubMed
-
- Dobson J. Drug Dev. Res. 2006, 67, 55–60.
-
- Alexis F.; Anker J. N. Ther. Delivery 2014, 5, 97–100. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
