A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study using Genz-644470 and sevelamer carbonate in hyperphosphatemic chronic kidney disease patients on hemodialysis
- PMID: 24748812
- PMCID: PMC3986335
- DOI: 10.2147/IJNRD.S56217
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study using Genz-644470 and sevelamer carbonate in hyperphosphatemic chronic kidney disease patients on hemodialysis
Abstract
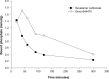
Background: Genz-644470 is a new, nonabsorbed phosphate binding polymer. In an in vitro competitive phosphate binding assay, Genz-644470 bound significantly more phosphate per gram than sevelamer. As a consequence, this clinical study evaluated the ability of Genz-644470 to lower serum phosphorus in patients on hemodialysis and compared serum phosphorus lowering of Genz-644470 with sevelamer carbonate and placebo. Because three different fixed doses of Genz-644470 and sevelamer carbonate were used, phosphate-lowering dose-responses of each agent were also analyzed.
Methods: A randomized, double-blind, dose-ranging study was conducted. After a 2-week phosphate binder washout, 349 hyperphosphatemic (serum phosphorus >5.5 mg/dL) hemodialysis patients were randomized to one of seven fixed-dose groups: placebo, Genz-644470 2.4 g/day, Genz-644470 4.8 g/day, Genz-644470 7.2 g/day, sevelamer carbonate 2.4 g/day, sevelamer carbonate 4.8 g/day, or sevelamer carbonate 7.2 g/day. Indicated total daily doses were administered in fixed divided doses three times a day with meals for 3 weeks. The change in serum phosphorus during the treatment period and its dose-response patterns were assessed.
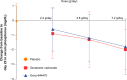
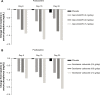
Results: Dose-dependent reductions in serum phosphorus were observed with both Genz-644470 and sevelamer carbonate. Serum phosphorus-lowering responses to fixed doses of sevelamer carbonate and Genz-644470 were enhanced in a roughly linear fashion with increasing doses over a threefold range after 3 weeks of treatment. Genz-644470 did not show any advantage in phosphorus lowering per gram of binder compared with sevelamer carbonate. Overall toler-ability was similar between active treatment groups. The tolerability of sevelamer carbonate was consistent with prior studies and with the established safety profile of sevelamer.
Conclusion: Both Genz-644470 and sevelamer carbonate effectively lowered serum phosphate levels in a dose-dependent fashion in patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis. However, Genz-644470 did not provide any advantage over sevelamer carbonate in phosphate lowering in vivo, as had been demonstrated in vitro.
Keywords: clinical trial; hemodialysis; serum phosphorus; sevelamer carbonate.
Figures
References
-
- Delmez J, Block G, Robertson J, et al. A randomized, double-blind, crossover design study of sevelamer hydrochloride and sevelamer carbonate in patients on hemodialysis. Clin Nephrol. 2007;68(6):386–391. - PubMed
-
- Young EW, Albert JM, Satayathum S, et al. Predictors and consequences of altered mineral metabolism: the Dialysis Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study. Kidney Int. 2005;67(3):1179–1187. - PubMed
-
- Tomasello S, Dhupar S, Sherman RA. Phosphate binders, K/DOQI guidelines, and compliance: the unfortunate reality. Dial Transplant. 2004;33(5):236–242.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

