Association of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Hepatitis B Virus-related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
- PMID: 24748895
- PMCID: PMC3989600
- DOI: 10.5812/hepatmon.16258
Association of Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Hepatitis B Virus-related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
Abstract
Background: Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is an important neuropsychiatry complication of acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). PPI therapy may increase the intestinal bacterial overgrowth and infections.
Objectives: The aim of this study was to assess whether PPI use in ACLF is associated with HE.
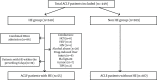
Patients and methods: A retrospective case-control study was performed. Fifty five admitted patients with hepatitis B virus (HBV)-related ACLF complicated by Stage II-IV HE developed after admission between January 2008 and December 2012 were matched (by sex, age, and MELD score) with comparable HBV-related ACLF patients (n = 110) who did not develop this complication during hospitalization. We excluded combined HE upon admission and other neurological disorders in patients with ACLF. Univariate and multivariate analyses of 30 variables (laboratory examination, predisposition, treatment, etc.) before the occurrence of HE were carried out to identify the factors predictive of HE.
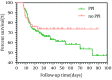
Results: In univariate analysis, patients with HE in ACLF had a significantly higher rate of PPI use (89.1%) compared with non-HE (63.6%, P = 0.001). In addition, clinical and standard laboratory variables were significantly different between the two groups regarding the infection rate, hyponatremia, alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), Arginine Hydrochloride use and Lactulose use. Logistic regression analysis was used to examine the combined effects of the variables with HE as the outcome. HE in ACLF was associated with hyponatremia (odds ratio (OR) = 6. 318, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 2. 803-14.241; P = 0. 000), PPI use was independently associated with HE (OR = 4. 392, CI = 1. 604-12.031; P = 0. 004), and lactulose use was protective (OR = 0. 294, CI = 0. 136-0.675; P = 0. 003).
Conclusions: The occurrence of HE is associated with hyponatremia and PPI use in patients with ACLF.
Keywords: Hepatic Encephalopathy; Hepatitis B Virus; Proton Pump Inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proton Pump Inhibitor Therapy Increases the Risk of Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis in Patients with HBV-Related Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure.Adv Ther. 2021 Sep;38(9):4675-4694. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01844-1. Epub 2021 Jul 25. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34308513
-
[Study on the application value of MELD-Na, CLIF-C OFs, COSSH-ACLFs and NLR scoring systems in patients with hepatitis B virus related acute-on-chronic liver failure].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Dec;32(12):1496-1501. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200720-00536. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33541504 Chinese.
-
[Value of a new predictive model in evaluating short-term prognosis of patients with hepatitis B virus related acute-on-chronic liver failure].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Aug;32(8):988-993. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200102-00075. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32912415 Chinese.
-
Characteristics, risk factors, and mortality of cirrhotic patients hospitalized for hepatic encephalopathy with and without acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF).J Hepatol. 2014 Feb;60(2):275-81. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.10.004. Epub 2013 Oct 12. J Hepatol. 2014. PMID: 24128414
-
A prognostic model for hepatitis B acute-on-chronic liver failure patients treated using a plasma exchange-centered liver support system.J Clin Apher. 2020 Apr;35(2):94-103. doi: 10.1002/jca.21762. Epub 2019 Nov 26. J Clin Apher. 2020. PMID: 31769901 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Association of proton pump inhibitors with risk of hepatic encephalopathy in advanced liver disease: A meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jun 7;25(21):2683-2698. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i21.2683. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31210719 Free PMC article.
-
Association of proton pump inhibitors with the risk of hepatic encephalopathy during hospitalization for liver cirrhosis.United European Gastroenterol J. 2018 Oct;6(8):1179-1187. doi: 10.1177/2050640618773564. Epub 2018 Apr 23. United European Gastroenterol J. 2018. PMID: 30288280 Free PMC article.
-
Proton pump inhibitor use increases hepatic encephalopathy risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jun 7;25(21):2675-2682. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i21.2675. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31210718 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation Between Proton Pump Inhibitors and the Complications of Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jan;33(1):44-52. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2022.20689. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35040787 Free PMC article.
-
Short-Term Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and Hepatic Encephalopathy Risk in Patients with Decompensated Cirrhosis.J Clin Med. 2019 Jul 25;8(8):1108. doi: 10.3390/jcm8081108. J Clin Med. 2019. PMID: 31349746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ong JP, Aggarwal A, Krieger D, Easley KA, Karafa MT, Van Lente F, et al. Correlation between ammonia levels and the severity of hepatic encephalopathy. Am J Med. 2003;114(3):188–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources