Regulatory role of regucalcin in heart calcium signaling: Insight into cardiac failure (Review)
- PMID: 24748964
- PMCID: PMC3990221
- DOI: 10.3892/br.2014.245
Regulatory role of regucalcin in heart calcium signaling: Insight into cardiac failure (Review)
Abstract
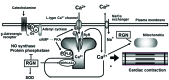
Regucalcin was first identified in 1978 as a regulatory protein of Ca2+ signaling in liver cells. Regucalcin was shown to play a multifunctional role in cell regulation, such as maintainance of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and suppression of signal transduction, protein synthesis, nuclear function, cell proliferation and apoptosis in various types of cells and tissues. Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling is based on the regulation of intracellular Ca2+ concentration by the Ca2+ pump in the sarcoplasmic reticulum of heart muscle cells. Regucalcin, which is expressed in the heart, was found to increase rat heart sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase activity and ATP-dependent Ca2+ uptake and mitochondrial Ca2+-ATPase activity. Regucalcin was also shown to suppress Ca2+-dependent protein tyrosine phosphatase, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase (calcineurin) and nitric oxide (NO) synthase activity in the heart cytoplasm. Moreover, regucalcin was found to activate superoxide dismutase (SOD), which plays a significant role in the prevention of cell death and apoptosis in the heart. Regucalcin may be a key molecule in heart muscle cell regulation through Ca2+ signaling. Regucalcin may also play a pathophysiological role in heart failure. The aim of this study was to review the recent findings regarding the role of regucalcin in Ca2+ signaling in the heart.
Keywords: Ca2+ signaling; Ca2+-ATPase; heart failure; nitric oxide synthase; regucalcin; sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase; superoxide dismutase.
Figures
References
-
- Yamaguchi M, Yamamoto T. Purification of calcium binding substance from soluble fraction of normal rat liver. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1978;26:1915–1918. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi M, Mori S. Effect of Ca2+and Zn2+on 5′-nucleotidase activity in rat liver plasma membranes: hepatic calcium-binding protein (regucalcin) reverses the Ca2+effect. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1988;36:321–325. - PubMed
-
- Yamaguchi M. A novel Ca2+-binding protein regucalcin and calcium inhibition. Regulatory role in liver cell function. In: Kohama K, editor. Calcium Inhibition. Japan Sci Soc Press, Tokyo and CRC Press; Boca Raton: 1992. pp. 19–41.
-
- Shimokawa N, Yamaguchi M. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the cDNA coding for a calcium-binding protein regucalcin from rat liver. FEBS Lett. 1993;327:251–255. - PubMed
-
- Shimokawa N, Matsuda Y, Yamaguchi M. Genomic cloning and chromosomal assignment of rat regucalcin gene. Mol Cell Biochem. 1995;151:157–163. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
