Arthroscopic capsular repair in the treatment of femoroacetabular impingement
- PMID: 24749018
- PMCID: PMC3986652
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eats.2013.08.006
Arthroscopic capsular repair in the treatment of femoroacetabular impingement
Abstract
The role of capsular repair in the arthroscopic treatment of femoroacetabular impingement remains poorly defined. Some surgeons rarely repair the capsule, whereas others perform repairs routinely. There is little direct clinical evidence to guide surgeon decision making. When capsular repairs are performed, the procedure requires adequate visualization and careful suture placement either to re-establish the patient's normal capsular volume or to plicate a redundant capsule in a hip with hyperlaxity preoperatively. We present our preferred technique for arthroscopic capsular repair.
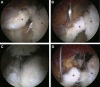
Figures


References
-
- Myers C.A., Register B.C., Lertwanich P. Role of the acetabular labrum and the iliofemoral ligament in hip stability: An in vitro biplane fluoroscopy study. Am J Sports Med. 2011;39(suppl):85S–91S. - PubMed
-
- Domb B.G., Philippon M.J., Giordano B.D. Arthroscopic capsulotomy, capsular repair, and capsular plication of the hip: Relation to atraumatic instability. Arthroscopy. 2013;29:162–173. - PubMed
-
- Ranawat A.S., McClincy M., Sekiya J.K. Anterior dislocation of the hip after arthroscopy in a patient with capsular laxity of the hip: A case report. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:192–197. - PubMed
-
- Matsuda D.K. Acute iatrogenic dislocation following hip impingement arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopy. 2009;25:400–405. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

