Action and therapeutic potential of oxyntomodulin
- PMID: 24749050
- PMCID: PMC3986661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2013.12.001
Action and therapeutic potential of oxyntomodulin
Abstract
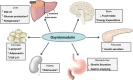
Oxyntomodulin (OXM) is a peptide hormone released from the gut in post-prandial state that activates both the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP1R) and the glucagon receptor (GCGR) resulting in superior body weight lowering to selective GLP1R agonists. OXM reduces food intake and increases energy expenditure in humans. While activation of the GCGR increases glucose production posing a hyperglycemic risk, the simultaneous activation of the GLP1R counteracts this effect. Acute OXM infusion improves glucose tolerance in T2DM patients making dual agonists of the GCGR and GLP1R new promising treatments for diabetes and obesity with the potential for weight loss and glucose lowering superior to that of GLP1R agonists.
Keywords: Body weight; GLP-1; Glucagon; Glucose metabolism; Oxyntomodulin.
Figures


References
-
- UKPDS U.K. prospective diabetes study 16. Overview of 6 years' therapy of type II diabetes: a progressive disease. U.K. Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Diabetes. 1995;44:1249–1258. - PubMed
-
- Bray G.A. Medical consequences of obesity. Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2004;89:2583–2589. - PubMed
-
- Holst J.J. Gut hormones as pharmaceuticals. From enteroglucagon to GLP-1 and GLP-2. Regulatory Peptides. 2000;93:45–51. - PubMed
-
- Hansen L., Hartmann B., Bisgaard T., Mineo H., Jørgensen P.N., Holst J.J. Somatostatin restrains the secretion of glucagon-like peptide-1 and -2 from isolated perfused porcine ileum. American Journal of Physiology – Endocrinology and Metabolism. 2000;278(6):E1010–E1018. - PubMed
-
- Nauck M.A., Kleine N., Orskov C., Holst J.J., Willms B., Creutzfeldt W. Normalization of fasting hyperglycaemia by exogenous glucagon-like peptide 1 (7-36 amide) in type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1993;36:741–744. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

