Adipokines - removing road blocks to obesity and diabetes therapy
- PMID: 24749053
- PMCID: PMC3986498
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molmet.2014.01.005
Adipokines - removing road blocks to obesity and diabetes therapy
Abstract
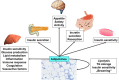
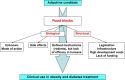
Prevention of obesity and therapeutic weight loss interventions have provided only limited long term success. Therefore there is an urgent need to develop novel pharmacological treatment strategies, which target mechanisms underlying positive energy balance, excessive fat accumulation and adverse fat distribution. Adipokines may have potential for future pharmacological treatment strategies of obesity and metabolic diseases, because they are involved in the regulation of appetite and satiety, energy expenditure, endothelial function, blood pressure, insulin sensitivity, adipogenesis, fat distribution and insulin secretion and others. There are important road blocks on the way from an adipokine candidate to the clinical use a therapeutic compound. Such road blocks include an incomplete understanding of the mechanism of action, resistance to a specific adipokine, side effects of the adipokine and others. This review focuses on the potential of selected adipokines as therapeutic tools or targets and discusses important road blocks, which currently prevent their clinical use.
Keywords: Adipokines; Adiponectin; Apelin; BMP7; DPP4; Leptin; Nampt/visfatin; Nesfatin-1; Obesity; Road blocks; Therapeutic compounds; Type 2 diabetes; Vaspin.
Figures

References
-
- Blüher M. Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology and Diabetes. 2009;117:241–250. - PubMed
-
- Van Gaal L.F., Mertens I.L., De Block C.E. Mechanisms linking obesity with cardiovascular disease. Nature. 2006;444:875–880. - PubMed
-
- LeRoith D., Novosyadlyy R., Gallagher E.J., Lann D., Vijayakumar A., Yakar S. Obesity and type 2 diabetes are associated with an increased risk of developing cancer and a worse prognosis; epidemiological and mechanistic evidence. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology and Diabetes. 2008;116(Suppl 1):S4–S6. - PubMed
-
- Sharma A.M., Padwal R. Obesity is a sign – over-eating is a symptom: an aetiological framework for the assessment and management of obesity. Obesity Reviews. 2010;11:362–370. - PubMed
-
- Ravussin E., Gautier J.F. Metabolic predictors of weight gain. International Journal of Obesity and Related Metabolic Disorders. 1999;23(Suppl. 1):S37–S41. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

